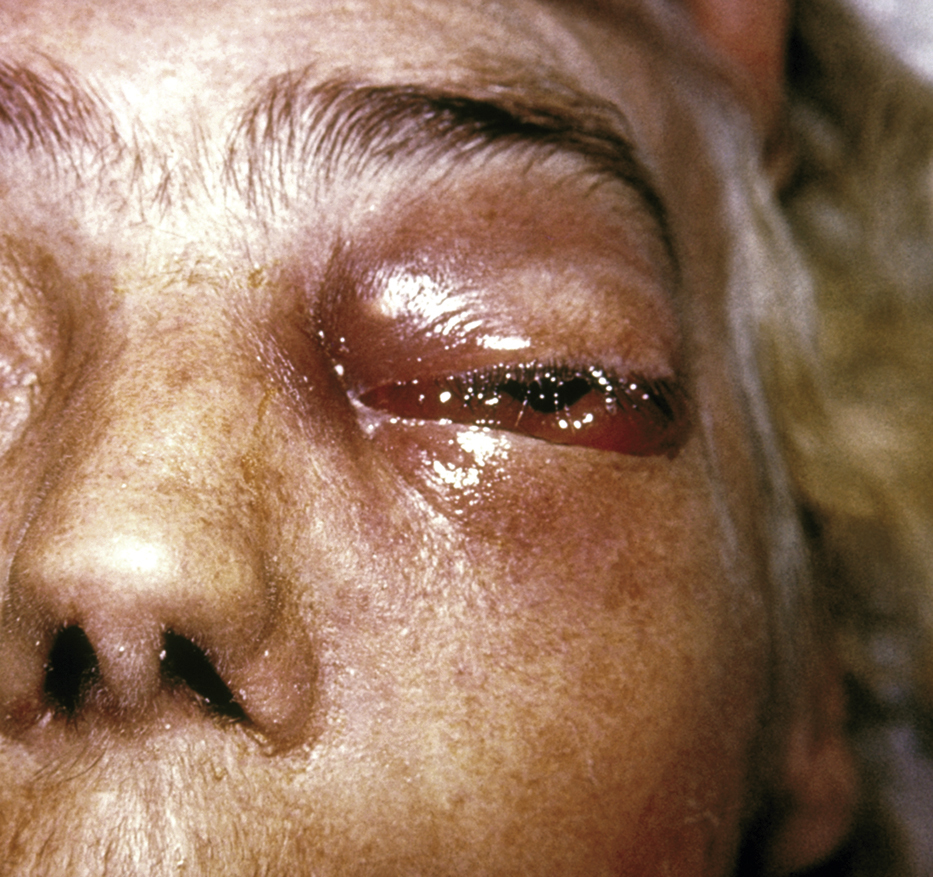
zygomycosis /zī′gōmīkō″sis/ [Gk, zygon + mykes, fungus] , an acute, often fulminant, and sometimes fatal fungal infections caused by a class of phycomycetal water molds in the orders Mucorales or Entomophthorales. They occur primarily in patients with chronic debilitating diseases, especially uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. The fungus may enter blood vessels and spread to the brain and other organs. Transmission is usually by inhalation. Kinds include mucormycosis, phycomycosis, basidiobolomycosis. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: The infection characteristically begins with fever, pain, and discharge in the nose and paranasal sinuses that progresses to invade the eye and lower respiratory tract. The diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy and pathological examination of sputum. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Treatment includes improved control of diabetes mellitus, extensive debridement of craniofacial lesions, and amphotericin B, administered intravenously. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: The disorder is also associated with natural disasters, when it is difficult to cleanse open wounds that are contaminated with soil or vegetative matter contaminated with a fungus.