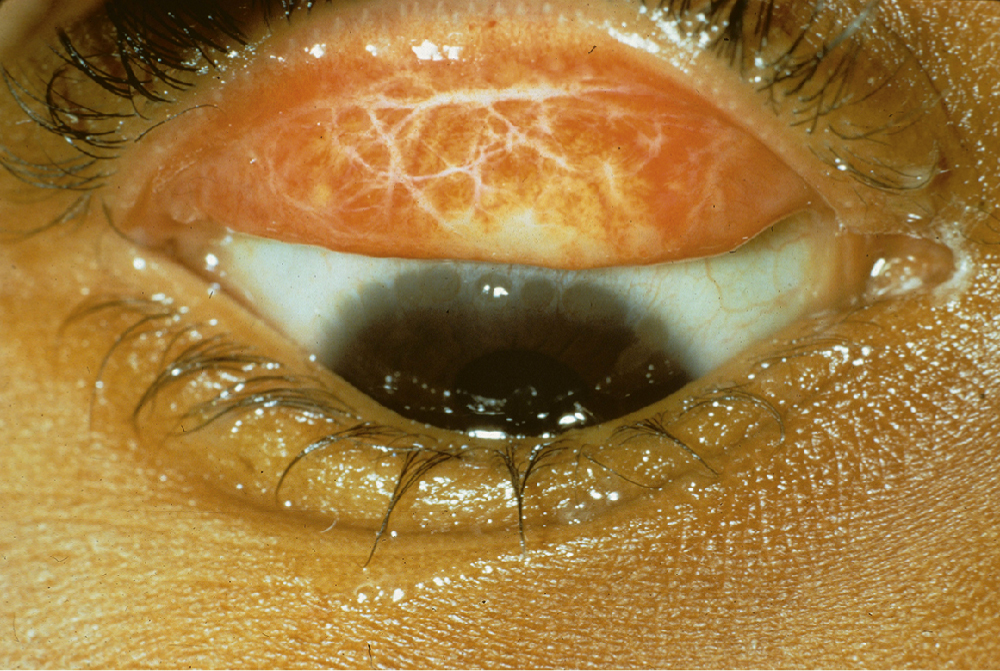
trachoma /trəkō″mə/ [Gk, roughness] , a chronic infectious disease of the eye caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. Also called Egyptian ophthalmia, granular conjunctivitis. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: It is characterized initially by inflammation, pain, photophobia, and lacrimation. If untreated, follicles form on the upper eyelids, forming scarring that causes trichiasis and corneal sequelae, eventually causing blindness. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: The current recommended treatment is the onetime use of use of oral azithromycin or the topical use of 1% tetracycline ointment. Scarred eyelids may be surgically repaired. Screening communities for the presence of trachoma in children 1 to 9 years of age is an important measure in the eradication of trachoma. When more than 10% of the community has the disease, the entire community is treated with antibiotics. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: Trachoma is a significant cause of blindness and is endemic to hot, dry, poverty-ridden areas. In the United States it is found in the Southwest. Teaching an affected population about the spread of trachoma, screening, and having an adequate water supply for washing hands, towels, and handkerchiefs are important factors in eliminating the disease.