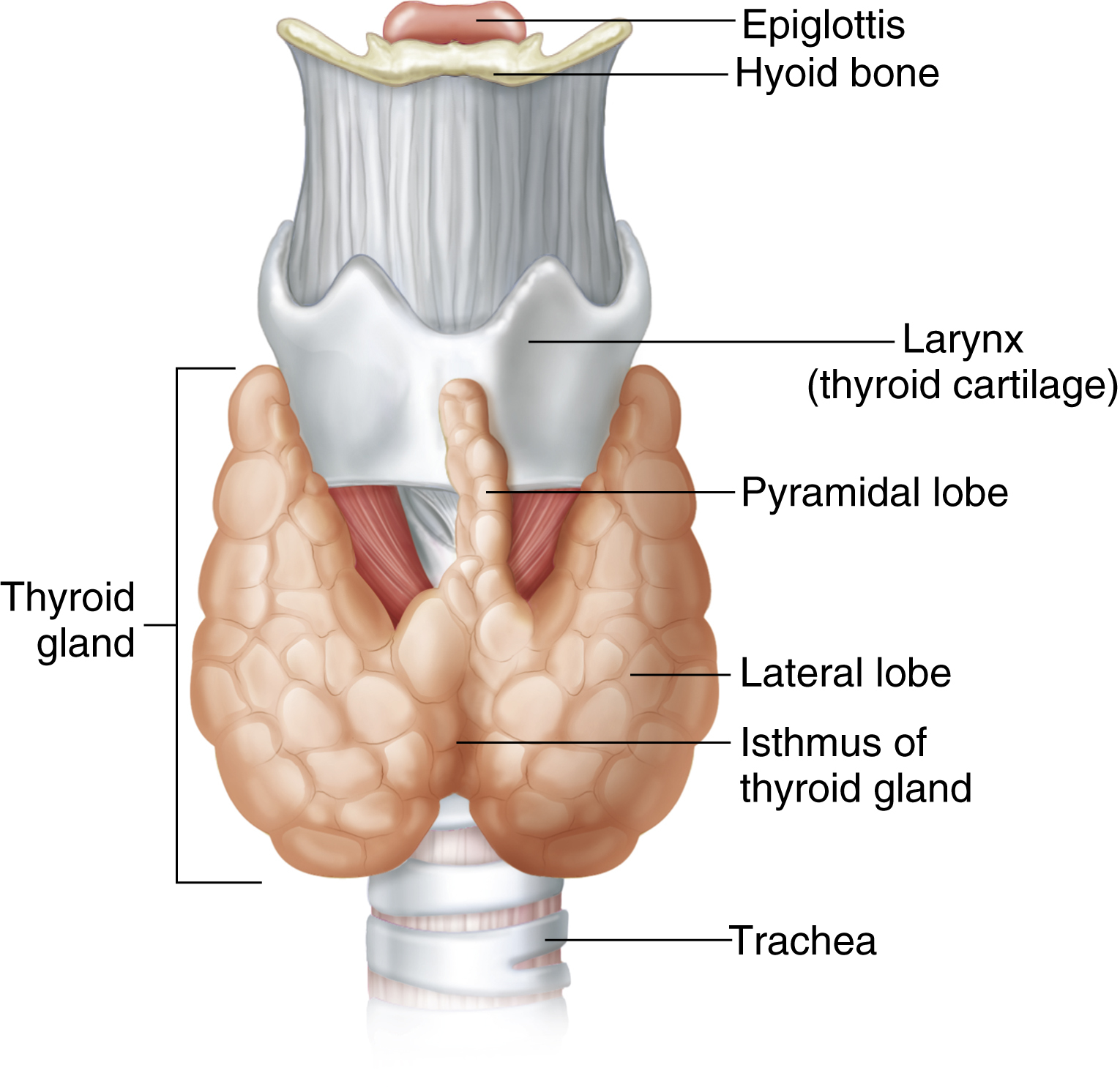
thyroid gland [Gk, thyreos, shield, eidos, form] , a highly vascular organ at the front of the neck, usually weighing about 30 g, consisting of bilateral lobes connected in the middle by a narrow isthmus. It is slightly heavier in women than in men and enlarges during pregnancy. The majority of the thyroid gland secretes the hormones thyroxin and triiodothyronine, and other clusters of cells produce the hormone calcitonin. These hormones are secreted directly into the blood; thus the thyroid is part of the endocrine system of ductless glands. It is essential to normal body growth in infancy and childhood, and its removal greatly reduces the oxidative processes of the body, producing a lower metabolic rate characteristic of hypothyroidism. The thyroid gland is activated by the pituitary thyrotrophic hormone and requires iodine to elaborate thyroxine. Also called thyroid. Compare parathyroid gland.