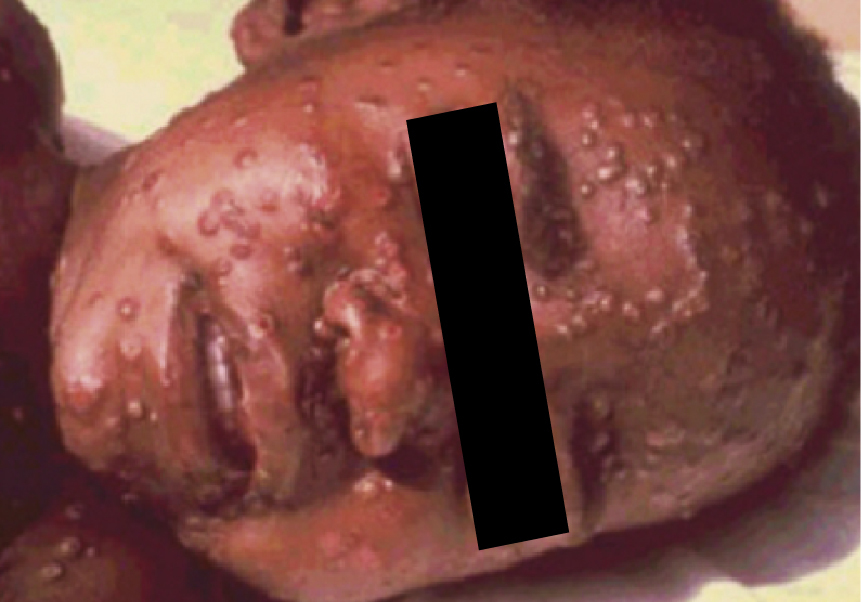
smallpox /smôl′poks/ [AS, smael + pocc] , a highly contagious and sometimes fatal viral disease characterized by fever, prostration, and a vesicular, pustular rash. It is caused by one of two species of poxvirus, variola minor (alastrim) or variola major, the latter being the severe and most common form. Because human beings are the only reservoir for the virus, worldwide vaccination with vaccinia, a related poxvirus, has been effective in eradicating smallpox; the last case of smallpox in the U.S. was in 1949, and the last recorded case in the world was in Somalia in 1977. The only known remaining sources of the virus are stored frozen at the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Smallpox is a potential agent for bioterrorism. Also called variola, variola major.