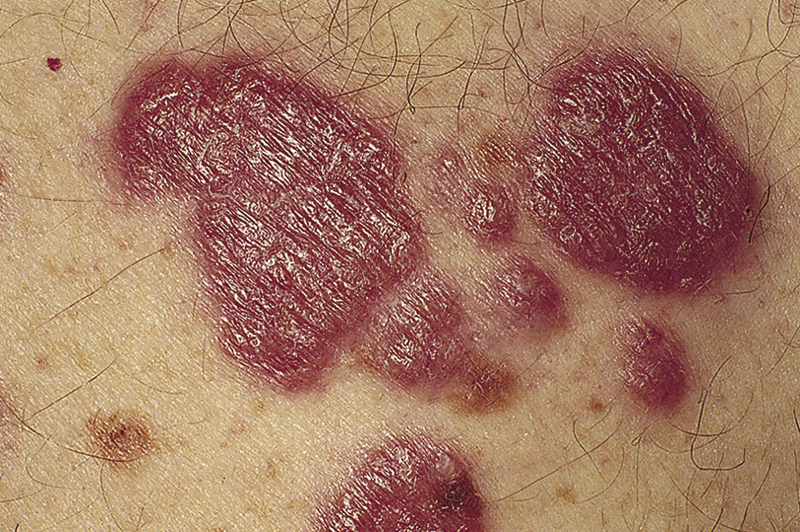
sarcoidosis /sär′koidō″sis/ [Gk, sarx, flesh, eidos, form, osis, condition] , a chronic disorder of unknown origin characterized by the formation of tubercles of nonnecrotizing epithelioid tissue. Common sites are the lungs, spleen, liver, skin, mucous membranes, and lacrimal and salivary glands, usually with involvement of the lymph glands. Diminished reactivity to tuberculin frequently accompanies the disorder. The lesions usually disappear over a period of months or years but may progress to widespread granulomatous inflammation and fibrosis. Also called sarcoid of Boeck.