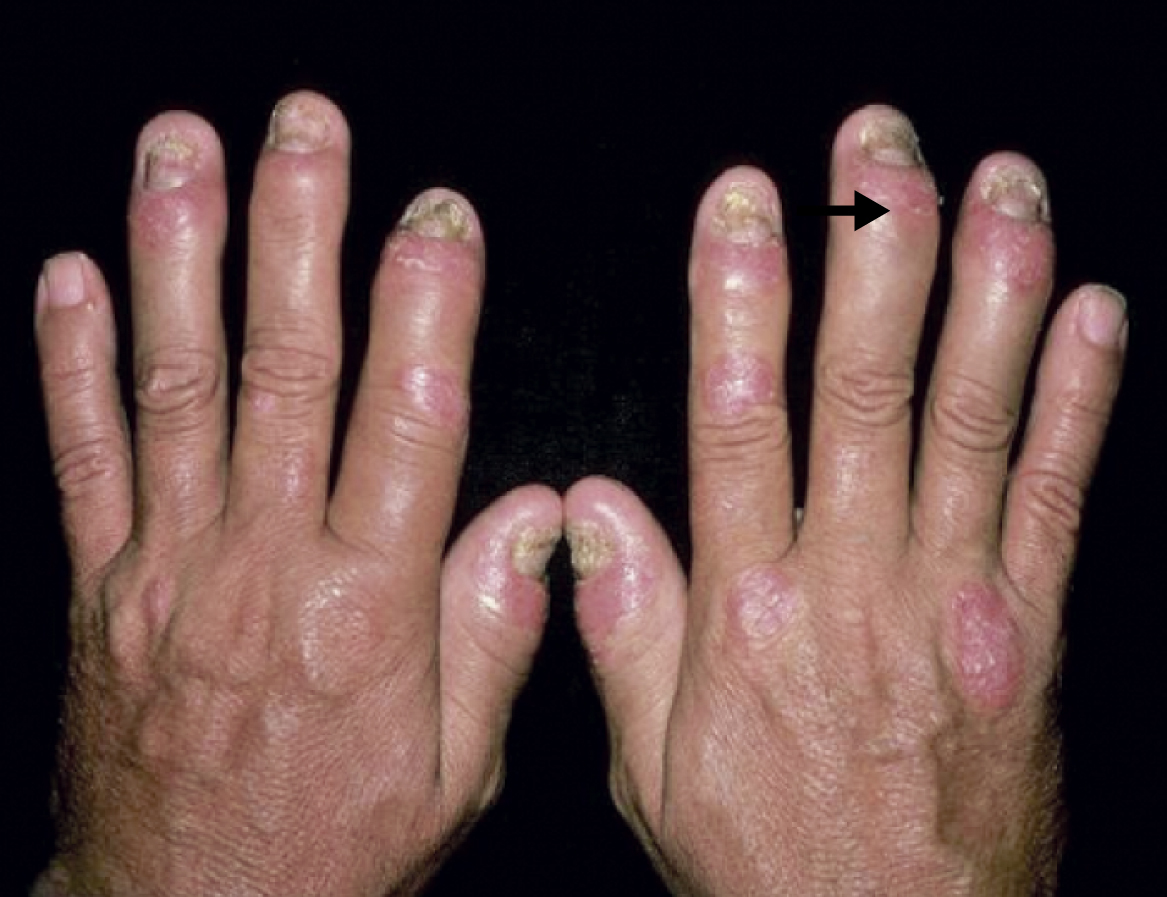
psoriatic arthritis /sôr′e·at″ik/ , a form of arthritis associated with psoriatic lesions of the skin and nails, particularly at the distal interphalangeal joints of the fingers and toes. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Stiffness and swelling, as well as joint pain, are the main symptoms of psoriatic arthritis. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: There is no cure; control of symptoms is the goal. Medications used to manage symptoms include nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), immunosuppressant medications, and TNF-alpha inhibitors. Members of the health care team should emphasize the importance of joint protection, maintenance of a healthy weight, and appropriate exercise. The control of stress is also an important intervention. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: Psoriatic arthritis can occur in people without psoriatic skin lesions. Activity is important, and the medications used to control symptoms can cause fatigue. The patient should be encouraged to remain active.