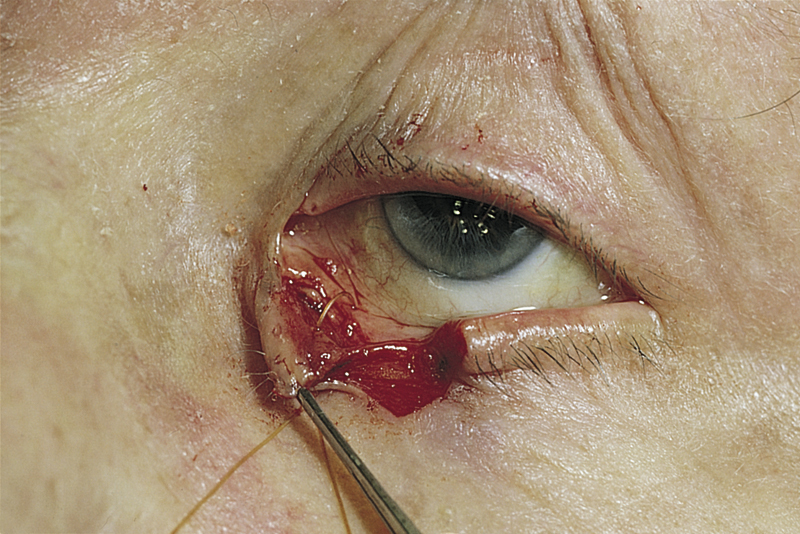
plastic surgery [Gk, plassein, to mold, cheirourgia, surgery] , surgery to heal, reconstruct, restore function, and correct disfigurement or scarring resulting from trauma or acquired or congenital lesions or defects. In performing corrective plastic surgery, the surgeon may use tissue from the patient or from another person or an inert material that is nonirritating, has a consistency appropriate to the use, and is able to hold its shape and form indefinitely. Implants are commonly used in mammoplasty for breast augmentation. Skin grafting is the most common procedure in plastic surgery. Z-plasty and Y-plasty are simpler techniques often performed instead of grafting in areas of the body covered by skin that is loose and elastic, such as the neck, axilla, throat, and inner aspect of the elbow. Dermabrasion is used to remove pockmarks, acne scars, or signs of traumatic skin damage. Chemical peeling is another technique in corrective plastic surgery. It is used primarily for removing fine wrinkles on the face. Tattooing, in which a pigment is tattooed into the skin of a graft, is performed to change the color of the graft to resemble more closely the surrounding skin. Reconstructive plastic surgery is performed to correct birth defects, to repair structures destroyed by trauma, and to replace tissue removed in other surgical procedures. Cleft lip and cleft palate repair and other maxillofacial surgical procedures, including rhinoplasty, otoplasty, and rhytidoplasty, are among these reconstructive procedures. Care of the patient before and after plastic surgery may require considerable sensitivity and tact. The patient may be exceedingly uncomfortable about the real or perceived appearance of the defect. An accepting, nonjudgmental attitude of all staff members is to the patient’s benefit. Optimal nutritional status helps a graft to “take” and speeds healing. Each procedure and technique involves particular kinds of care in the preoperative and postoperative periods. Instructions and assistance in self-care activities are also specific to the procedure. Success of most of the procedures depends greatly on the patient’s cooperation and on fastidious nursing care. The correction of a visible abnormality may be of inestimable benefit to the patient’s assurance, self-esteem, and function in society. Also called cosmetic surgery, reconstructive surgery. See also specific procedures.