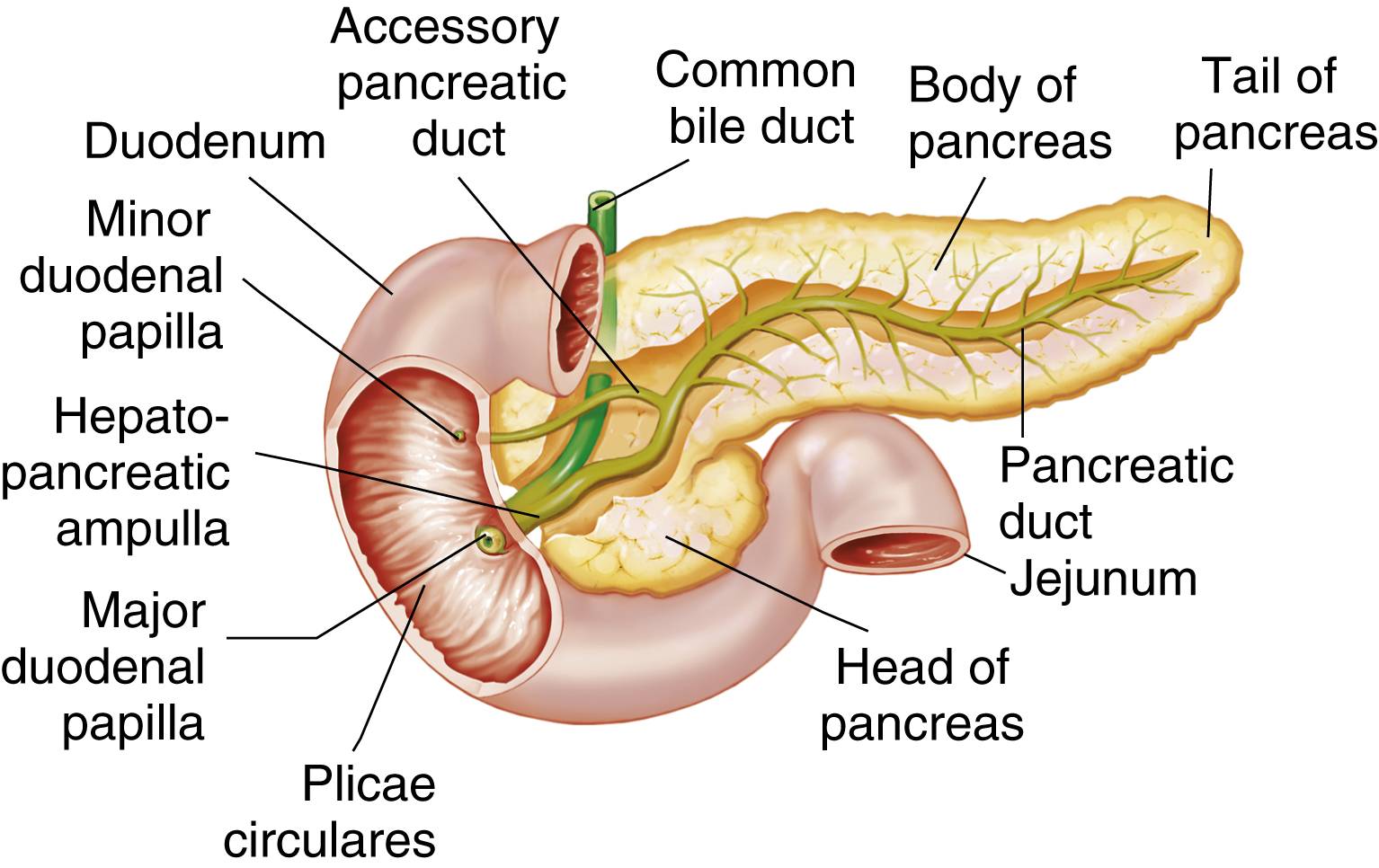
pancreas /pan″krē·əs/ [Gk, pan, all, kreas, flesh] , an elongated grayish pink lobulated gland that stretches transversely across the posterior abdominal wall in the epigastric and hypochondriac regions of the body and secretes various substances, such as digestive enzymes, insulin, and glucagon. It is divided into a head; a flattened, elongated body; and a tail in contact with the spleen. The head of the gland, divided from the body by a small constriction, is tucked into the curve of the duodenum. The tapered left extremity of the organ forms the tail. In adults the pancreas is about 13 cm long. A compound, mixed gland composed of exocrine and endocrine tissue, it contains a main duct that runs the length of the organ, draining smaller ducts and emptying into the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla, the same site that accommodates the entrance of the common bile duct.