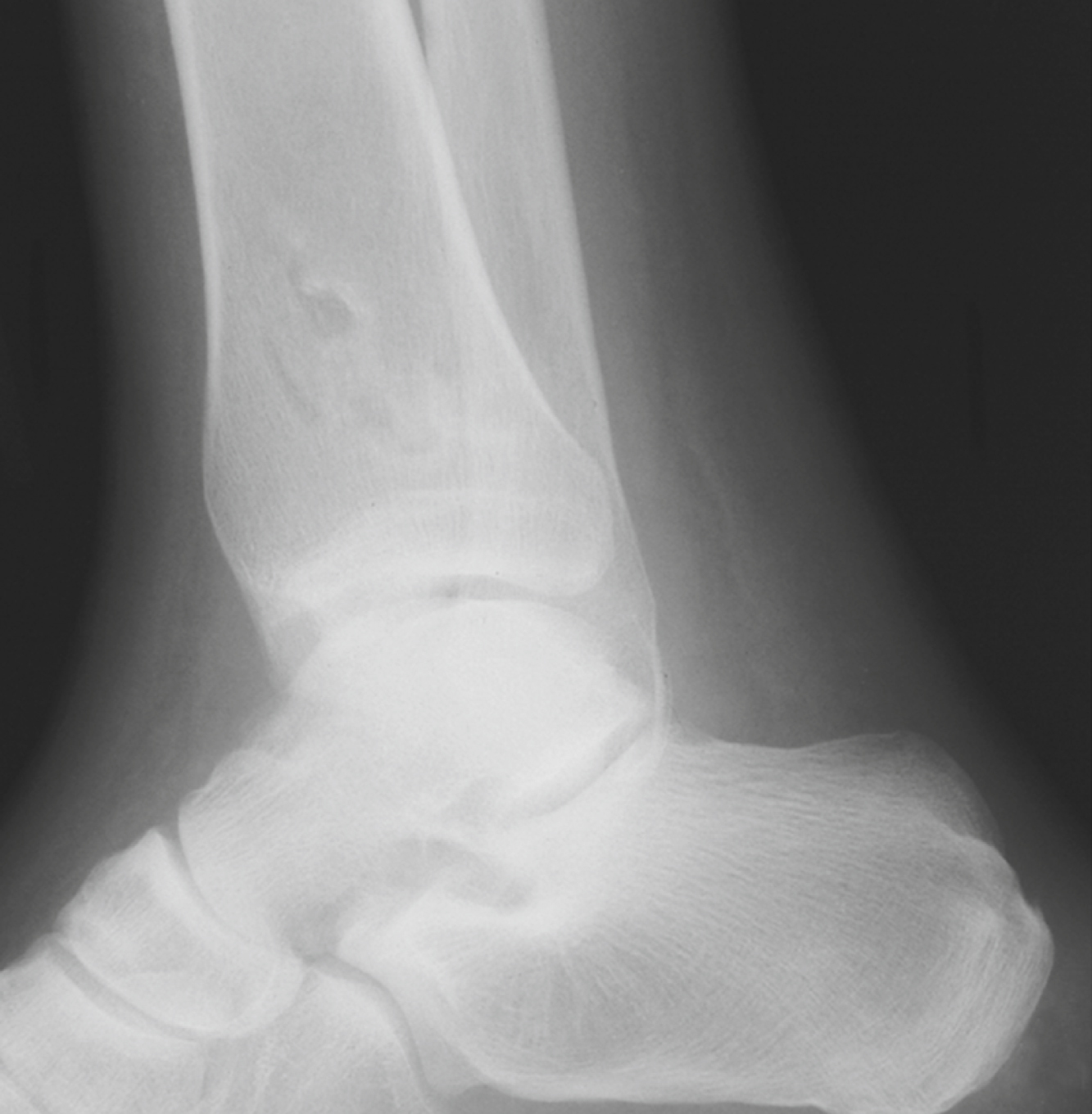
osteomyelitis /-mī·əlī″tis/ [Gk, osteon + myelos, marrow, itis, inflammation] , local or generalized infection of bone and bone marrow, usually caused by bacteria introduced by trauma or surgery, by direct extension from a nearby infection, or via the bloodstream. Staphylococci are the most common causative agents. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: The long bones in children and the vertebrae in adults are the most common sites of infection as a result of hematogenous spread. Persistent, severe, and increasing bone pain; tenderness; guarding on movement; regional muscle spasm; and fever suggest this diagnosis. Draining sinus tracts may accompany posttraumatic osteomyelitis or osteomyelitis from a contiguous infection. Specific diagnosis and selection of therapy depend on bacterial examination of bone, tissue, or pus. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Treatment includes bed rest and parenteral antibiotics for several weeks. Surgery may be necessary to remove necrotic bone and tissue, obliterate cavities, remove infected prosthetic appliances, and apply prostheses to stabilize affected parts. Chronic osteomyelitis may persist for years with exacerbations and remissions despite treatment. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: Normal precautions are used in disposing of any drainage. Absolute rest of the affected part may be necessary, with a careful positioning using pillows and sandbags for good alignment. During the early phase of infection, pain is extremely severe, and extraordinary gentleness in moving and manipulating the infected part is essential.