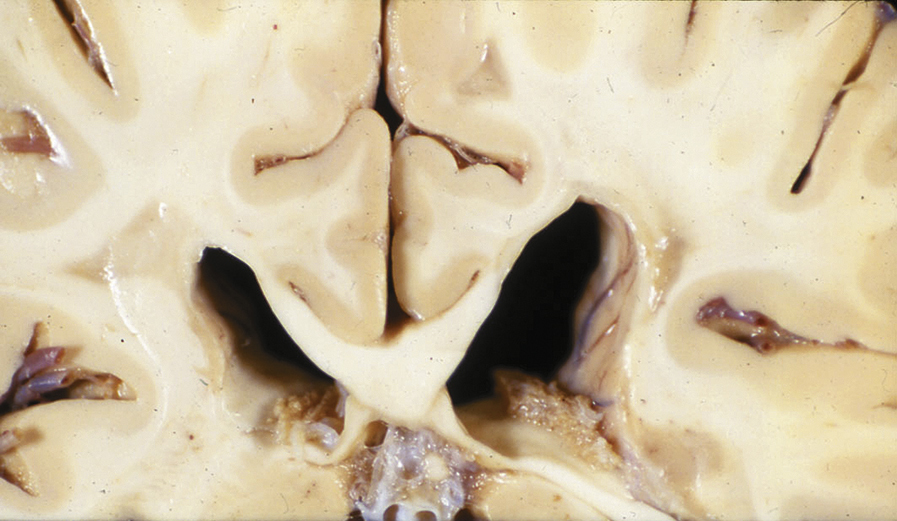
multiple sclerosis (MS) [L, multus + plica, fold; Gk, sklerosis, hardening] , a progressive disease characterized by disseminated demyelination of nerve fibers of the brain and spinal cord. Multifocal lesions of plaque destroy the myelin and to a varying degree, oligodendrocytes. It begins slowly, usually in young adulthood, and continues throughout life with periods of exacerbation and remission. The first signs are often paresthesias, or abnormal sensations in the extremities or on one side of the face. Other early signs are muscle weakness, vertigo, and visual disturbances, such as nystagmus, diplopia (double vision), and partial blindness. Later in the course of the disease there may be extreme emotional lability, ataxia, abnormal reflexes, and difficulty in urinating. A history of exacerbation and remission of symptoms and the presence of greater-than-normal amounts of protein in cerebrospinal fluid are characteristic. Most of the brain and spinal cord will show characteristic lesions. As the disease progresses, the intervals between exacerbations grow shorter and disability becomes greater. Treatment involves drugs that affect the function of the immune system; acute episodes, also called exacerbations, are often treated with corticosteroids. Physical therapy may help postpone or prevent specific disabilities. The patient is encouraged to live as normal and active a life as possible. Also called disseminated multiple sclerosis.