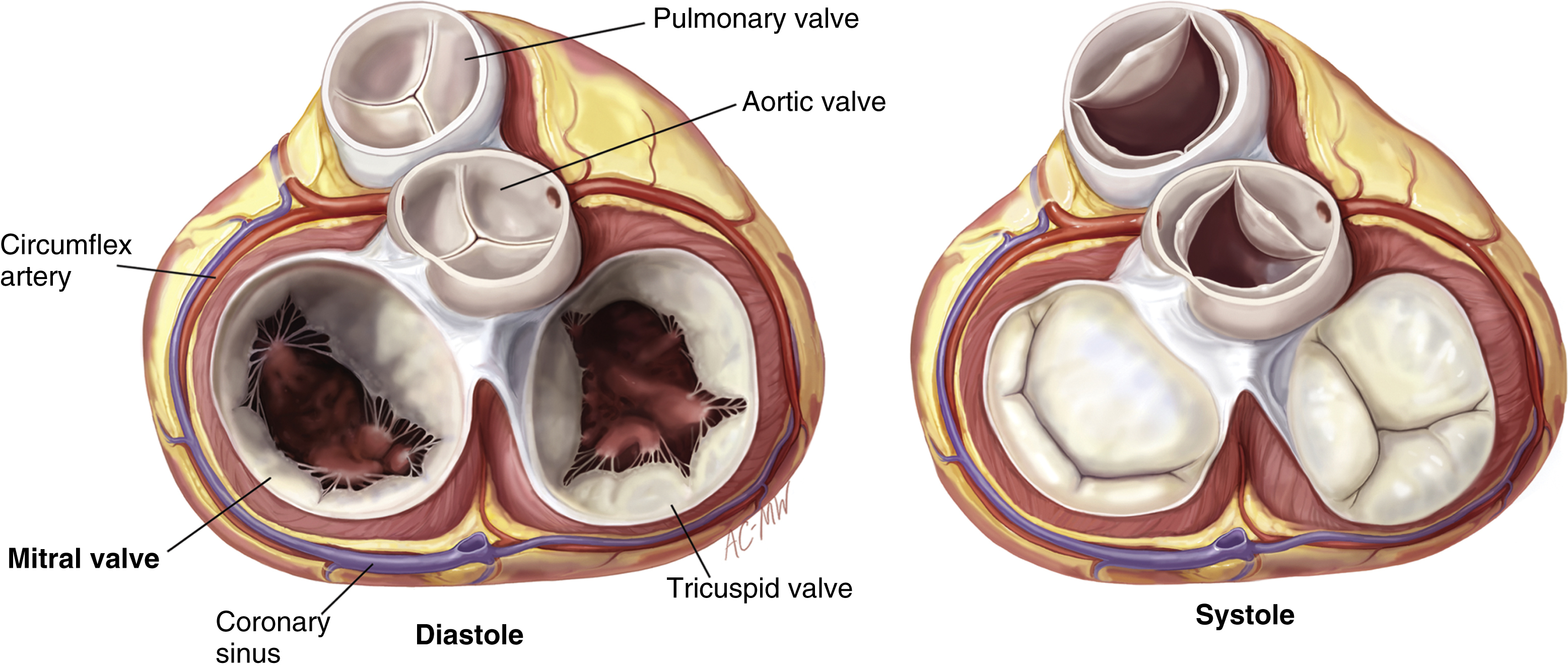
mitral valve, a bicuspid valve situated between the left atrium and the left ventricle; the only valve with two, rather than three, cusps. The mitral valve allows blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle but prevents blood from flowing back into the atrium. Ventricular contraction in systole forces the blood against the valve, closing the two cusps and assuring the flow of blood from the ventricle into the aorta. The ventral cusp of the mitral valve is longer than the dorsal cusp. Also called bicuspid valve, left atrioventricular valve. Compare aortic valve, pulmonary valve, semilunar valve, tricuspid valve.