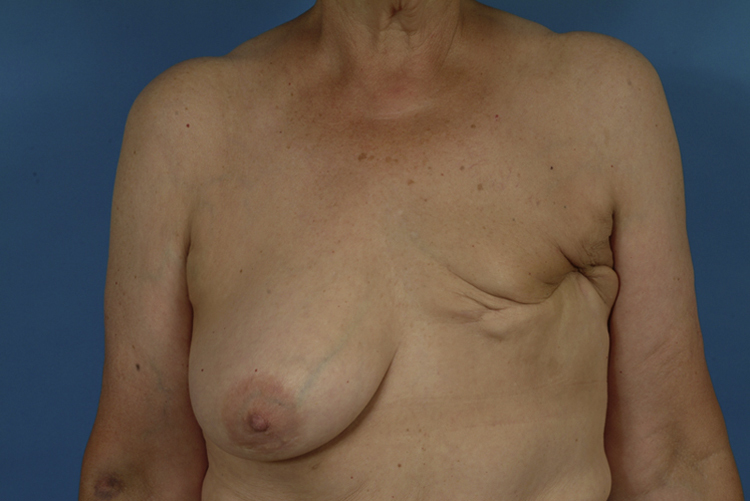
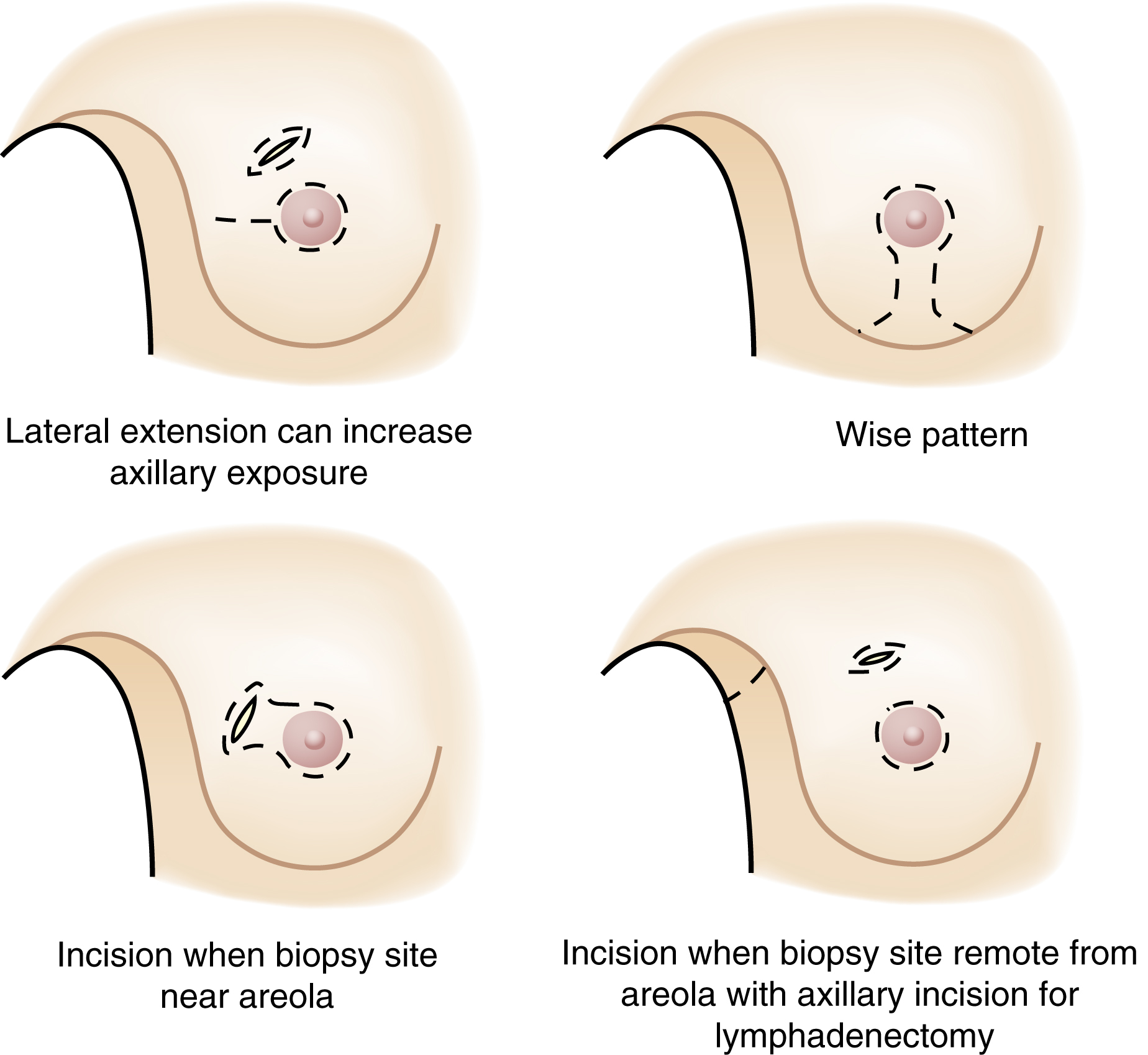
mastectomy /mastek″təmē/ [Gk, mastos, breast, ektomē, excision] , the surgical removal of one or both breasts, most commonly performed to remove a malignant tumor. In a simple mastectomy the breast is removed without lymph node dissection. In a radical mastectomy some of the muscles of the chest are removed with the breast, together with lymph nodes in the axilla. In a modified radical mastectomy the involved breast and all axillary contents (axillary, pectoral, and superior apical nodes) are removed, but the pectoral muscles are preserved. The tumor is biopsied before the mastectomy. If the specimen shows a malignancy, the tumor and adjacent tissues are removed in one piece. At the end of the surgical procedure a drainage catheter is placed in the wound. The nurse inspects the wound for swelling or excessive bleeding and encourages the patient to deep breathe. The affected arm is positioned with the hand pointed upward or on pillows so that the hand is higher than the lower arm, with the lower arm above heart level to promote venous return. Hand and wrist movements and elbow flexion and extension are begun within 24 hours and performed regularly. The patient may be fitted with a prosthesis when the wound is completely healed or at the time of the mastectomy. Blood pressures and venipuncture may not be performed on the side of the mastectomy. Emotional support and counseling are essential. See also breast cancer, modified radical mastectomy, radical mastectomy, simple mastectomy.