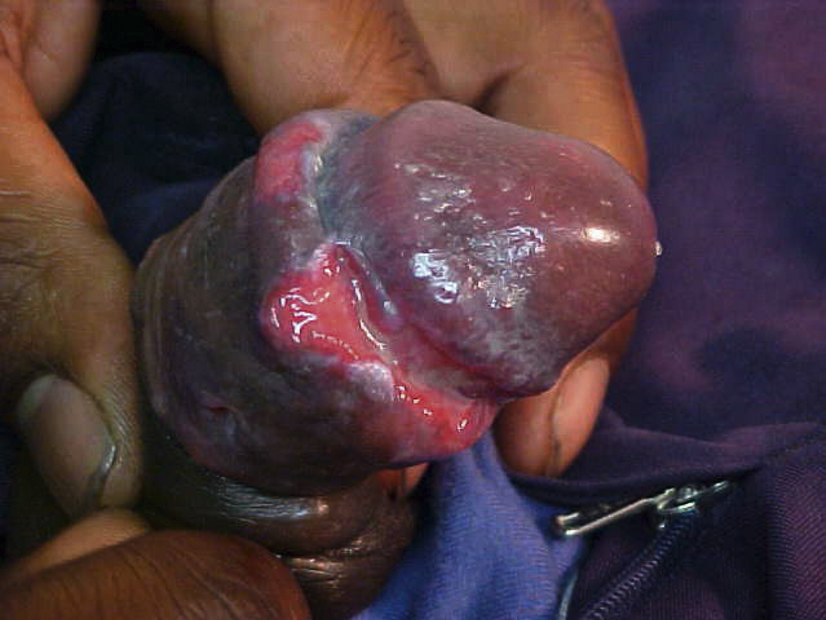
lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) /-gran′yəlō″mə/ [L, lympha + granulum, small grain; Gk, oma, tumor; L, Venus, goddess of love] , a sexually transmitted disease caused by a strain of the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis that primarily infects the lymphatics. It is characterized by ulcerative genital lesions, marked swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin, headache, fever, and malaise. Ulcerations of the rectal wall occur less commonly. The disease is diagnosed by isolating the organism from an infected node and demonstrating LGV antibodies by serological blood test. Doxycycline is usually prescribed for the patient and any person with whom there has been sexual contact. Also called lymphopathia venereum. See also Chlamydia.