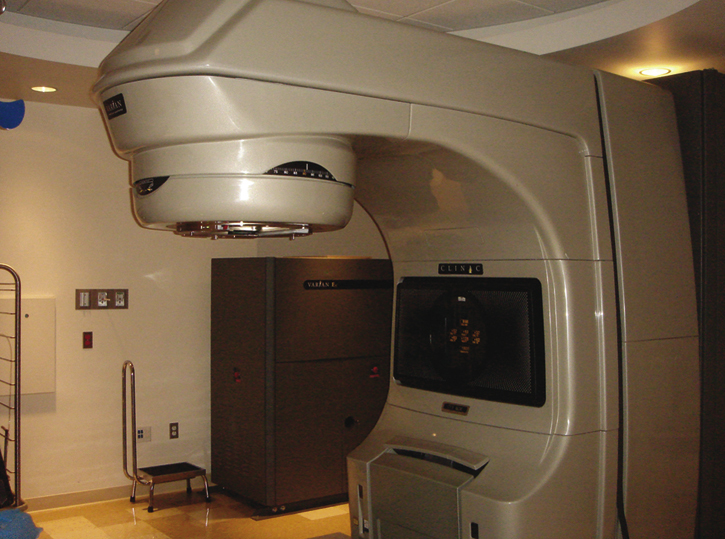
linear accelerator (LINAC) [L, linea, line, accelerare, to quicken] , an apparatus for accelerating charged subatomic particles, used in radiotherapy, physics research, and the production of radionuclides. A pulsed electron beam generated by an electron gun passes through a long, straight vacuum tube containing alternating hollow electrodes. The electrodes are arranged so that when their high-frequency potentials are properly varied, the electrons passing through the tube receive successive increments of energy. The electrons are stopped abruptly by a heavy metal target at the end of the tube and directed by a collimator to deliver supervoltage x-rays to the patient receiving radiotherapy.