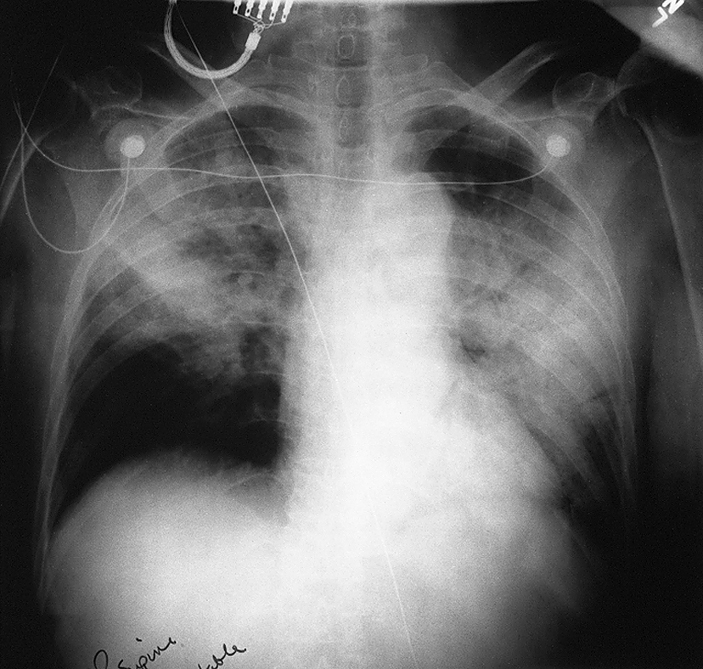
Legionnaires’ disease /lē′jənerz″/ [American Legion] , an acute bacterial pneumonia caused by infection with Legionella pneumophila. It is characterized by an influenzalike illness followed within a week by high fever, chills, muscle aches, and headache. The symptoms may progress to dry cough, pleurisy, and sometimes diarrhea. Usually the disease is self-limited, but mortality has been 15% to 20% in a few localized epidemics. Contaminated air-conditioning cooling towers and warm stagnant water supplies, including water vaporizers, water sonicators, whirlpool spas, and showers, may be sources of organisms. Person-to-person contagion has not occurred. Risk of infection is increased by the presence of other conditions, such as cardiopulmonary diseases. Treatment includes supportive care and antibiotic therapy. Also called legionellosis.