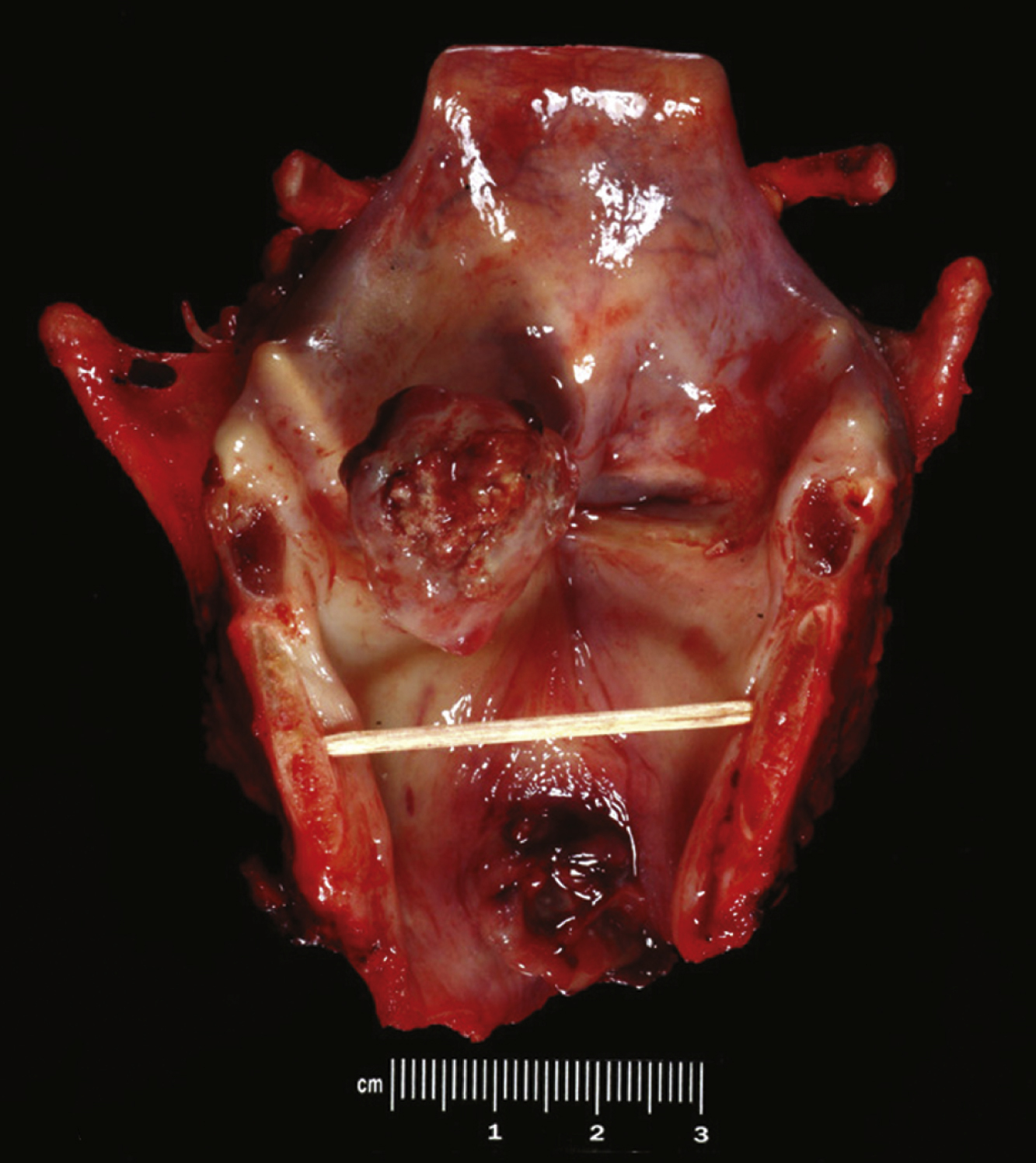
laryngeal cancer [Gk, larynx + L, cancer, crab] , a malignant neoplastic disease characterized by a tumor arising from the epithelium of the structures of the larynx. Laryngeal tumors are more common in men than in women and occur most frequently between 50 and 70 years of age. Chronic alcoholism and heavy use of tobacco increase the risk of developing the cancer. Persistent hoarseness is usually the first sign. Advanced lesions may cause a sore throat, dyspnea, dysphagia, and cervical adenopathy. Diagnostic measures include direct laryngoscopy, biopsy, MRI, and radiological examination, including tomographic studies and chest films. Malignant tumors of the larynx are usually epidermoid carcinomas. Radiation is generally recommended for small lesions. Total laryngectomy, often combined with radiotherapy, is indicated for extensive lesions. Chemotherapy may be used to try to spare the larynx. After the operation a speech therapist will assist the individual to develop a new sound source for speech. See also laryngectomy.