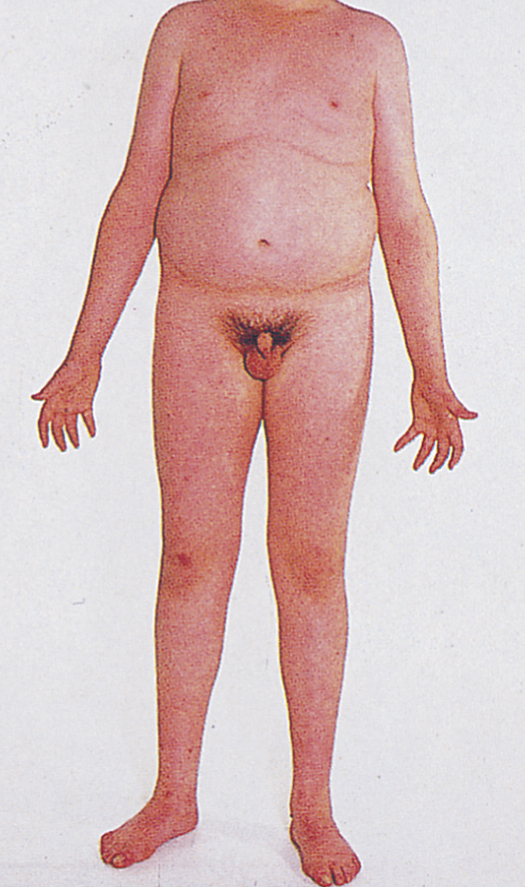
Klinefelter’s syndrome /klīn″feltərz/ [Harry F. Klinefelter, American physician, 1912–1990] , a condition of gonadal defects appearing in males after puberty, caused by an extra X chromosome in at least one cell line. Characteristics are small firm testes, long legs, gynecomastia, poor social adaptation, subnormal intelligence, chronic pulmonary disease, and varicose veins. The severity of the abnormalities increases with greater numbers of X chromosomes. The most common abnormality is a 47 XXY karyotype. Men with the karyotype XXXXY have marked congenital malformations and cognitive impairment.