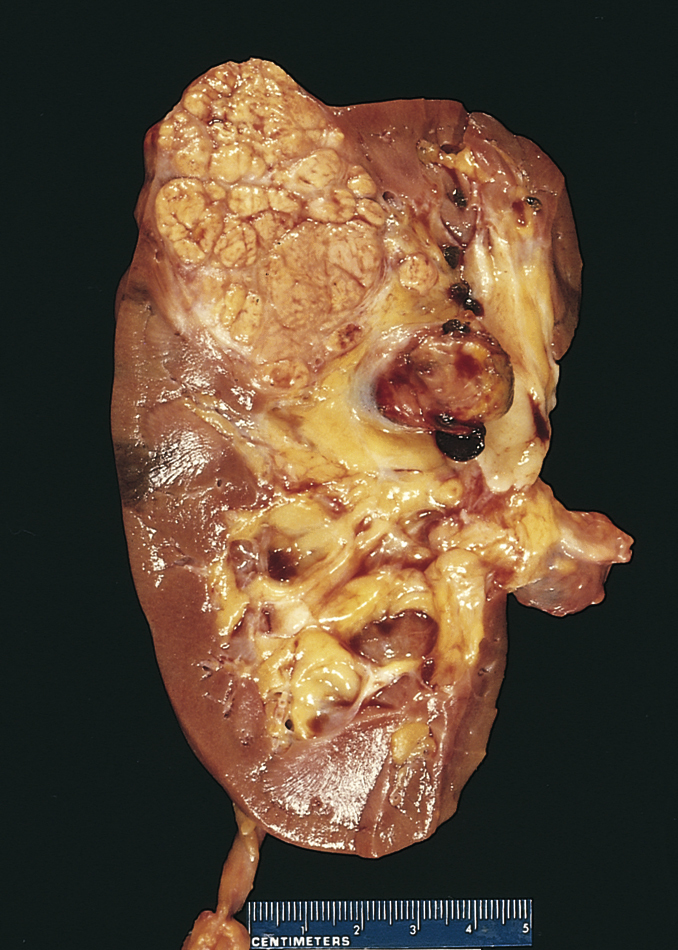
kidney cancer, a malignant neoplasm of the renal parenchyma or renal pelvis. Factors associated with an increased incidence of disease are exposure to aromatic hydrocarbons or tobacco smoke. A long asymptomatic period may precede the onset of the characteristic symptoms, which include hematuria, flank pain, fever, and a palpable mass. Diagnostic measures include urinalysis, excretory urography, nephrotomography, ultrasonography, renal arteriography, and microscopic and cytological studies of cells from the renal pelvis. Adenocarcinoma of the renal parenchyma accounts for 80% of kidney tumors, occurring twice as frequently in men as in women; transitional cell or squamous cell carcinomas in the renal pelvis account for approximately 15% and are equally frequent in both men and women. Radical nephrectomy with lymph node dissection is usually recommended for tumors of the parenchyma. Nephroureterectomy is usually recommended for operable tumors of the renal pelvis. Radiotherapy may be used before or after surgery and as palliation for inoperable tumors. Chemotherapeutic agents may induce temporary remission. See also renal cell carcinoma, Wilms’ tumor.