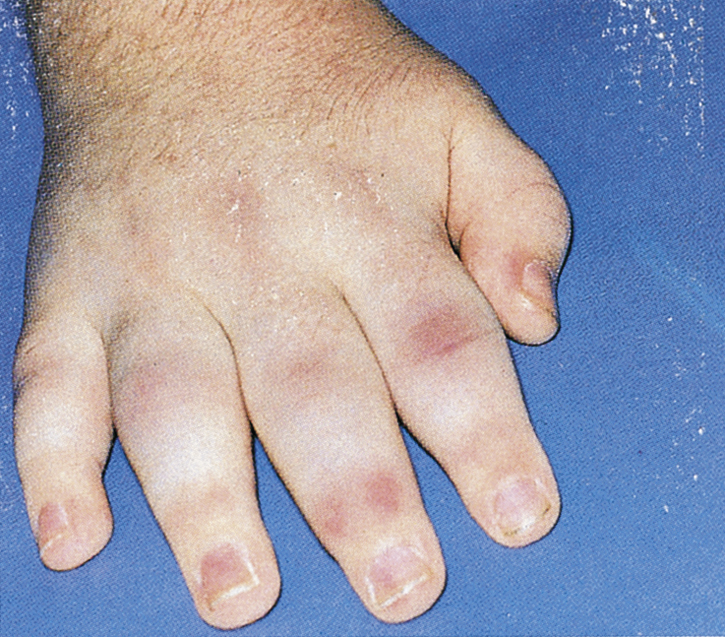
juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA), a form of rheumatoid arthritis, usually affecting the larger joints of children younger than 16 years of age and often accompanied by systemic manifestations. As bone growth in children is dependent on the epiphyseal plates of the distal epiphyses, skeletal development may be impaired if these structures are damaged. Treatment is supportive and includes analgesia, antiinflammatory medication, and rest. Also called Still’s disease.