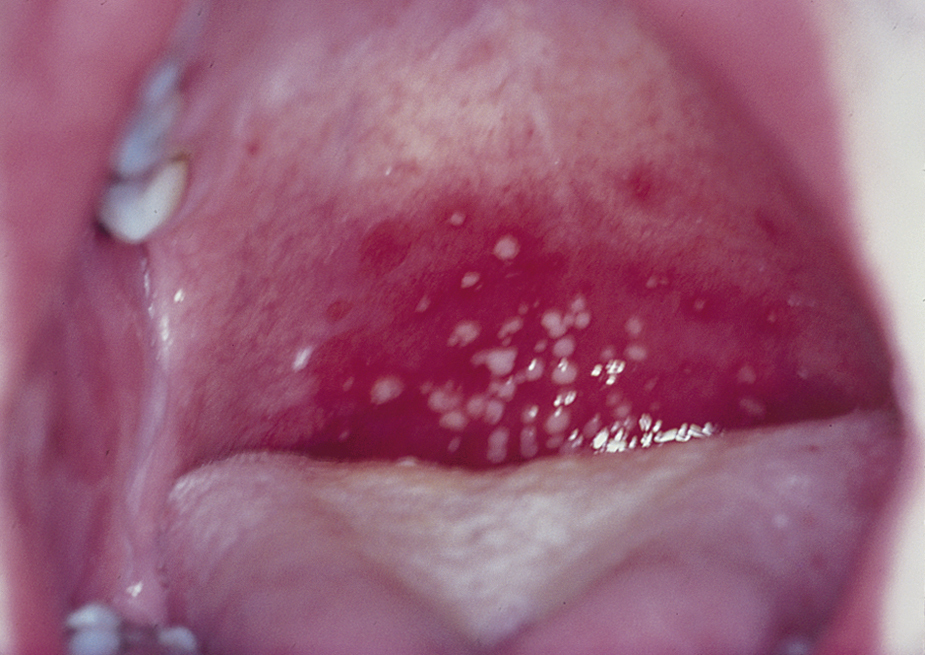
herpangina /hur′panjī″nə/ [Gk, herpein, to creep; L, angina, quinsy] , a viral infection, usually of young children, characterized by sore throat, headache, anorexia, and pain in the abdomen, neck, and extremities. Febrile convulsions and vomiting may occur in infants. Papules or vesicles may form in the pharynx and on the tongue, the palate, or the tonsils. The lesions evolve into shallow ulcers that heal spontaneously. The disease usually runs its course in less than 1 week. Treatment is symptomatic. The cause is often infection by a strain of coxsackie virus, typically coxsackie virus A. If similar shallow, blister-like lesions appear on the soles of the feet or the palms of the hands, it is called hand-foot-and-mouth disease.