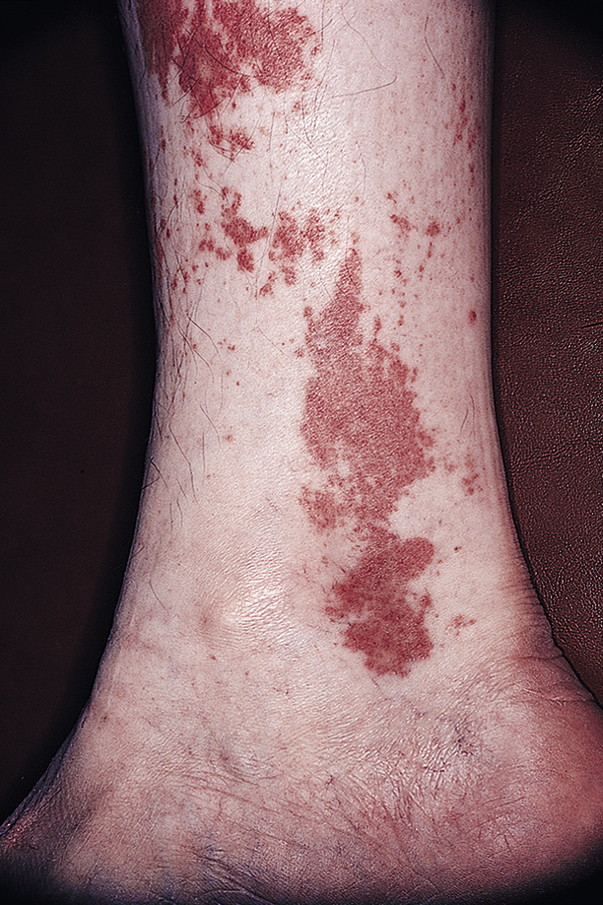
Henoch-Schönlein purpura /hen″ôkh shœn″līn/ [Eduard H. Henoch, German physician, 1820–1910; Johannes L. Schönlein, German physician, 1793–1864] , a self-limited hypersensitivity vasculitis, chiefly of children, characterized by purpuric skin lesions that appear predominantly on the lower abdomen, buttocks, and legs and are usually associated with pain in the knees and ankles. Other joint involvement, GI bleeding, and hematuria are also common findings. The disease lasts up to 6 weeks and has no sequelae if renal involvement is not severe. Immunosuppressive drugs, such as corticosteroids, may help relieve the nephropathy. Also called anaphylactoid purpura, Henoch-Schönlein syndrome, Schönlein-Henoch purpura.