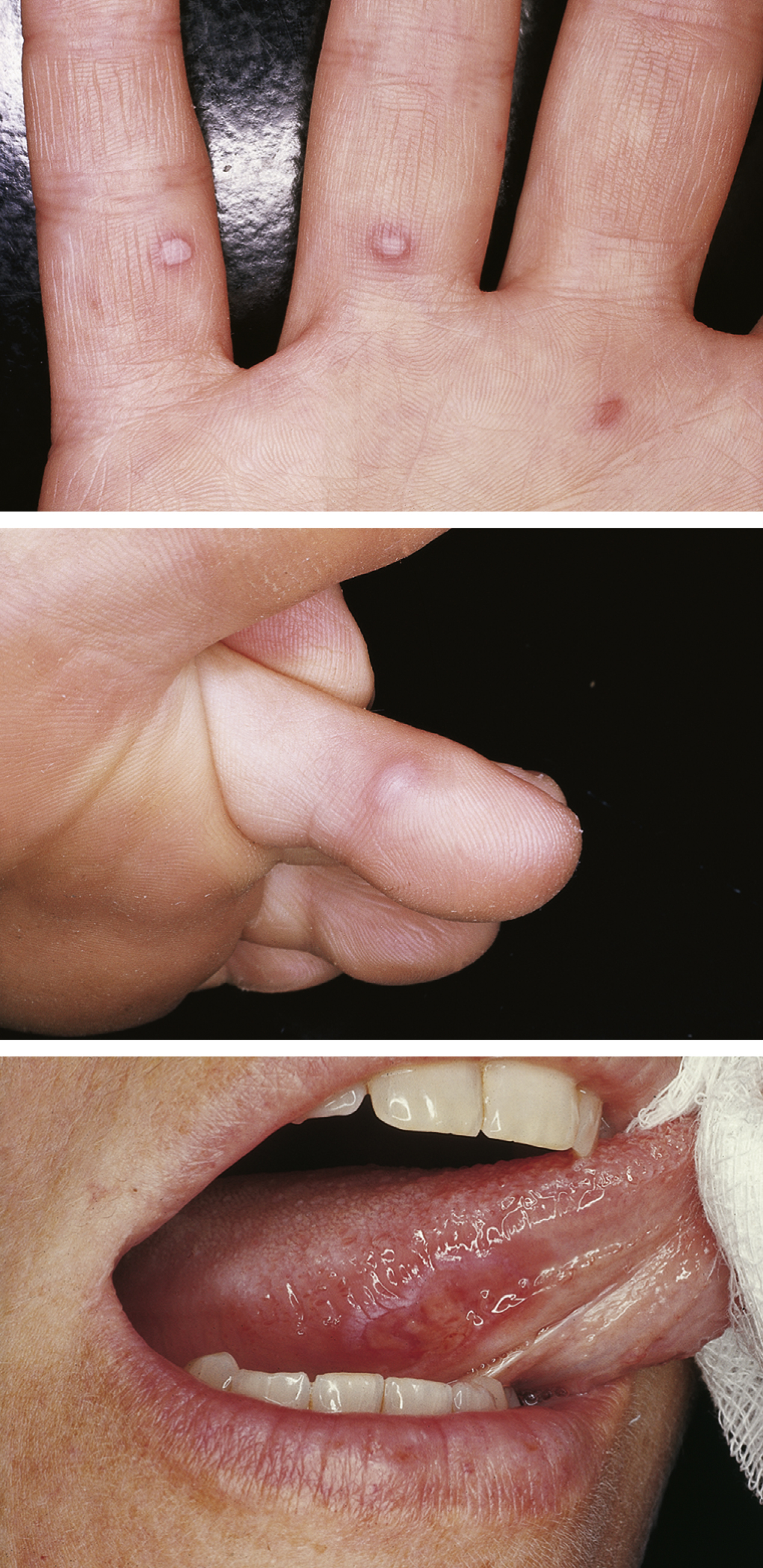
hand-foot-and-mouth disease, a viral infection usually caused by coxsackie A virus but also by enterovirus 71. It is characterized by the appearance of painful ulcers and vesicles on the mucous membranes of the mouth and on the hands and feet. The disease is very contagious and mainly affects children, including infants. There is no specific treatment. It is spread through contact with oral secretions (respiratory droplets) or stool. Lesions usually resolve in 1 week. Antiseptic mouthwashes and simple analgesics can be used to relieve discomfort of eating. It should not be confused with foot-and-mouth disease, which is primarily an animal disease.