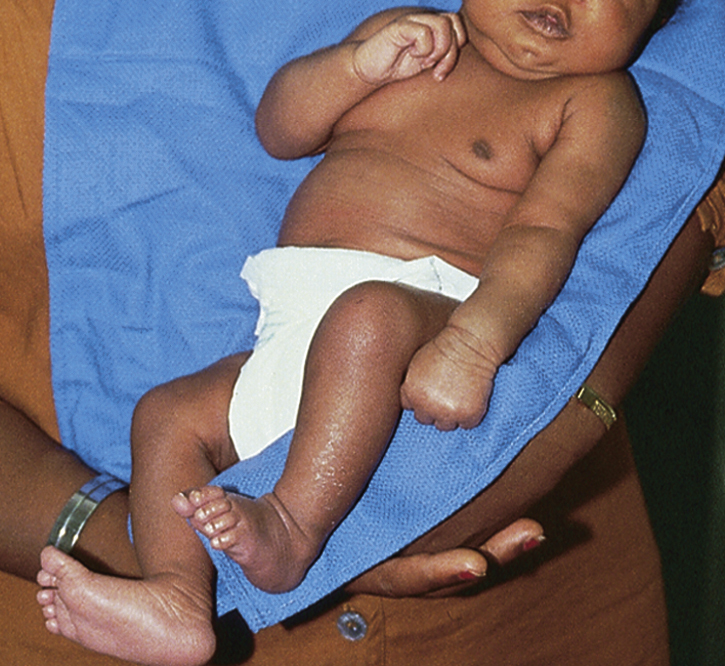
Erb’s palsy [Wilhelm H. Erb, German neurologist, 1840–1921] , a kind of paralysis caused by traumatic injury to the upper brachial plexus. It occurs most commonly as a result of forcible traction during childbirth, with injury to one or more cervical nerve roots. The signs of Erb’s palsy include loss of sensation in the arm and paralysis and atrophy of the deltoid, the biceps, and the brachialis muscles. The arm on the affected side hangs loosely with the elbow extended and the forearm pronated. Treatment initially requires that the arm and shoulder be immobilized to allow the swelling and inflammation of the associated neuritis to resolve. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and splinting may be necessary to improve muscle function and to prevent flexion contracture of the elbow. Also called Erb-Duchenne paralysis.