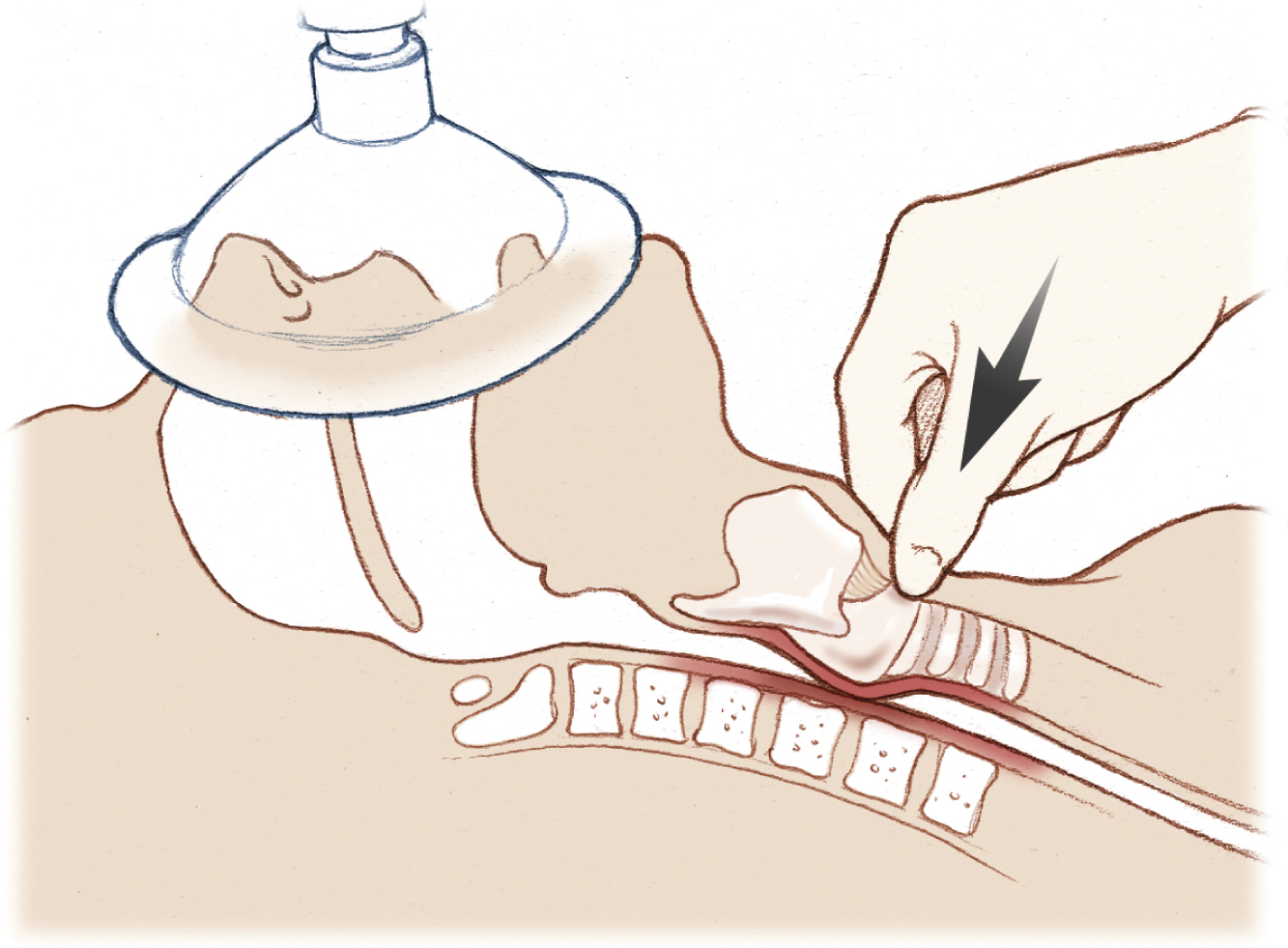
cricoid pressure, a technique to reduce the risk of the aspiration of stomach contents during induction of general anesthesia. The cricoid cartilage is pushed against the body of the sixth cervical vertebra, compressing the esophagus to prevent passive regurgitation. The technique cannot, however, and should not be used to stop active vomiting. Cricoid pressure is applied before intubation, immediately after injection of anesthetic drugs, and as a part of “rapid sequence” intubation. Once a mainstay of aspiration prevention, the effectiveness of this technique has recently been called into question. Cricoid pressure may also be used to move the larynx posteriorly and/or superiorly to facilitate visualization during laryngoscopy. Also called Sellick’s maneuver.