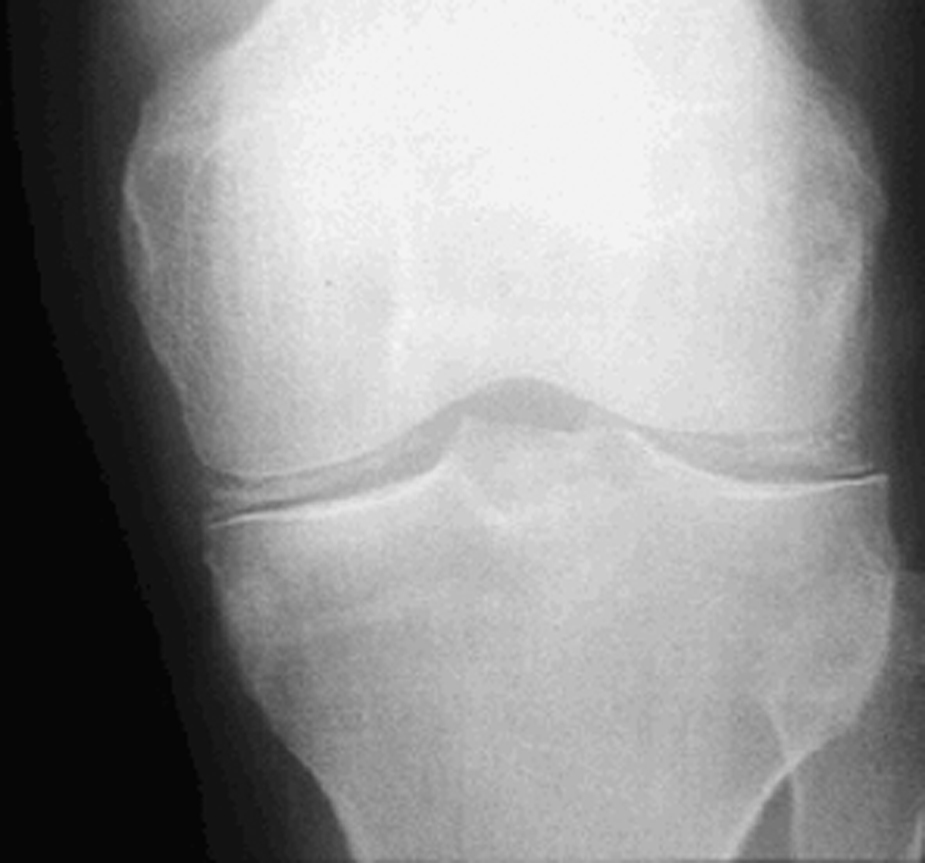
chondrocalcinosis /kon′drōkal′sinō″sis/ [Gk, chondros + L, calyx, lime; Gk, osis, condition] , an arthritic disease in which calcium deposits are present in the peripheral joints. It resembles gout and often occurs in patients over 50 years of age who have osteoarthritis or diabetes mellitus. It most commonly invades the knee joint. Aspiration of synovial fluid from the affected joints reveals crystals of calcium salts, especially calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate. Inflammation and pain may be relieved by intraarticular injections of hydrocortisone and by antiinflammatory medications. Also called pseudogout. Compare gout.