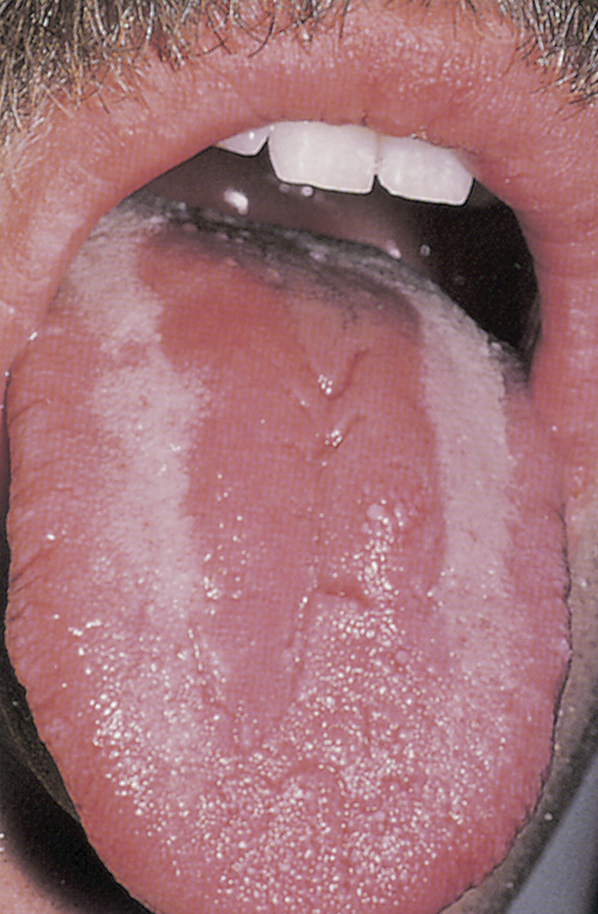
candidiasis /kan′didī″əsis/ [L, candidus + Gk, osis, condition] , any infection caused by a species of Candida, usually Candida albicans. The nails, rectum, and skin folds are sites of infection. Diaper rash, intertrigo, vaginitis, conjunctivitis, and thrush are common topical manifestations of candidiasis. Oral candidiasis without a history of recent antibiotic therapy, cytotoxic therapy, corticosteroid therapy, radiation therapy to the head and neck, or immunosuppressive disorder may indicate the possibility of human immunodeficiency virus infection. The most common source for candidemia is the GI tract and intravascular catheters. Also called candidosis, moniliasis. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: This common form of vaginitis presents with a thick, cheesy white or yellow discharge, intense itching, and redness and swelling of labia and vulva. Symptoms exacerbate in the week that precedes menses, and menstruation provides some relief of the itching. Diagnosis is based on symptomatology and positive wet mount or culture. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Treatment targets the infective agent with the use of topical and/or oral antifungal agents. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: Instruction in correct use of vaginal applications of medications is needed. Stress should be placed on the need to complete the full course of antifungal treatment. Education should include the importance of vaginal hygiene/cleanliness to prevent an environment for pathogen growth. Douching should be avoided, because it destroys the protective vaginal environment. Tight, nonporous, nonabsorbent underclothing should be avoided.