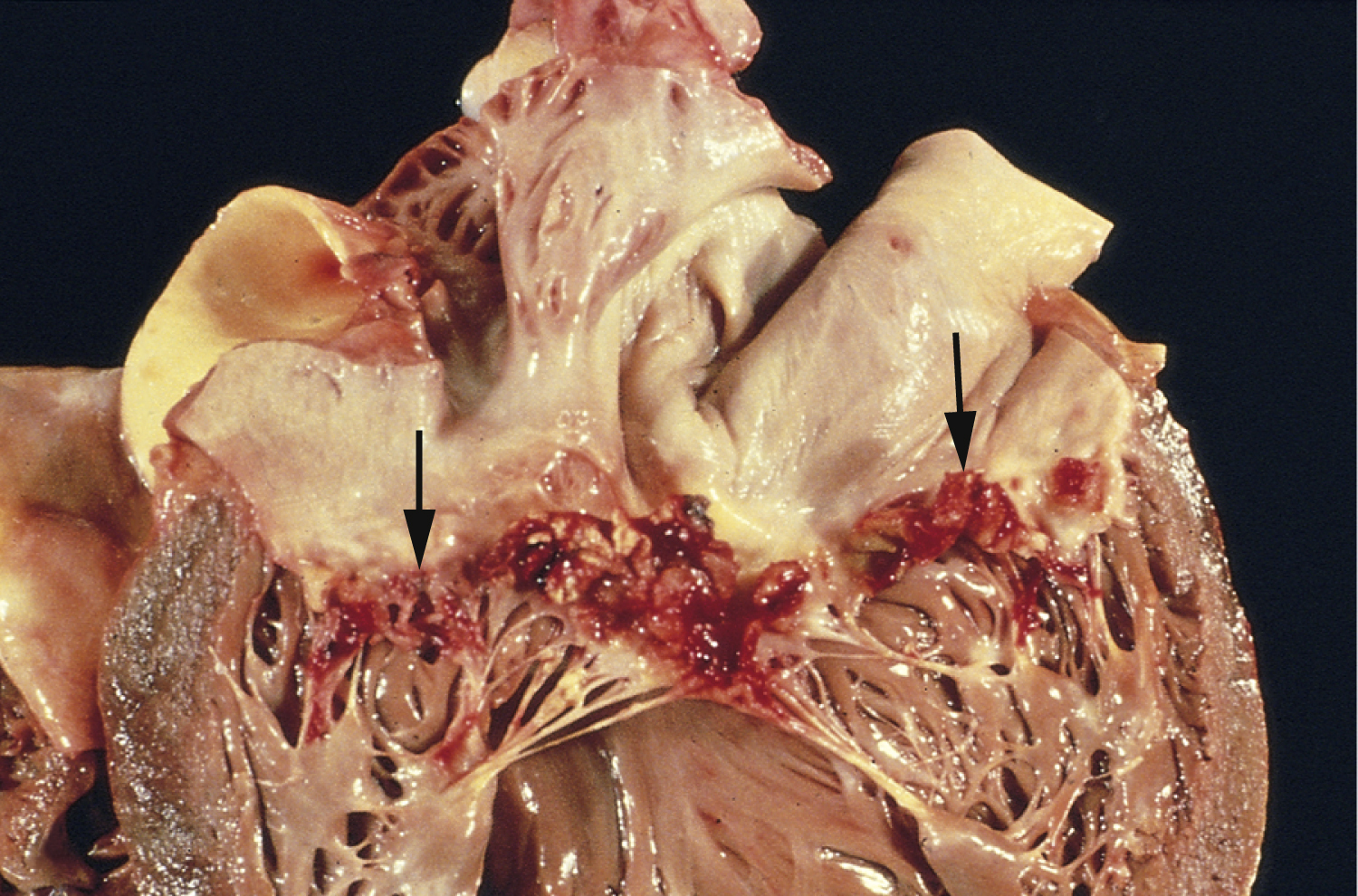
bacterial endocarditis, an acute or subacute bacterial infection of the endocardium or the heart valves or both. See also endocarditis, subacute bacterial endocarditis. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: The condition is characterized by heart murmur, prolonged fever, bacteremia, splenomegaly, and embolic phenomena. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Prompt treatment of both types with antibiotics, such as penicillin, cephalosporin, or gentamicin given intravenously, is essential to prevent destruction of the valves and cardiac failure. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: The acute variety progresses rapidly and is usually caused by staphylococci. The subacute variety is usually caused by the lodging of Streptococcus viridans in heart valves damaged by rheumatic fever.