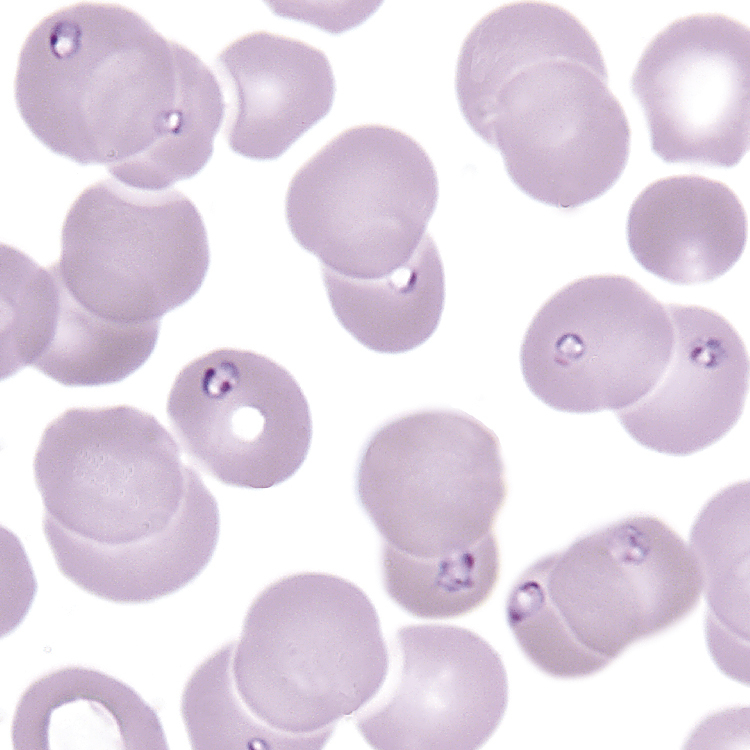
babesiosis /bəbē′sē·ō″sis/ [Victor Babés, Romanian bacteriologist, 1854–1926] , a potentially severe and sometimes fatal disease caused by infection with protozoa of the genus Babesia. The parasite is introduced into the host through the bite of ticks and infects red blood cells. In the United States, incidence of the disease is highest in the Northeast and North Central regions. Symptoms include headache, fever, chills, vomiting, hepatosplenomegaly, hemolytic anemia, fatigue, myalgia, and hemolysis. Treatment is clindamycin or quinone. Most patients with babesiosis are asymptomatic. Approximately 25% of patients with babesiosis are also infected with Lyme disease. Also called babesiasis.