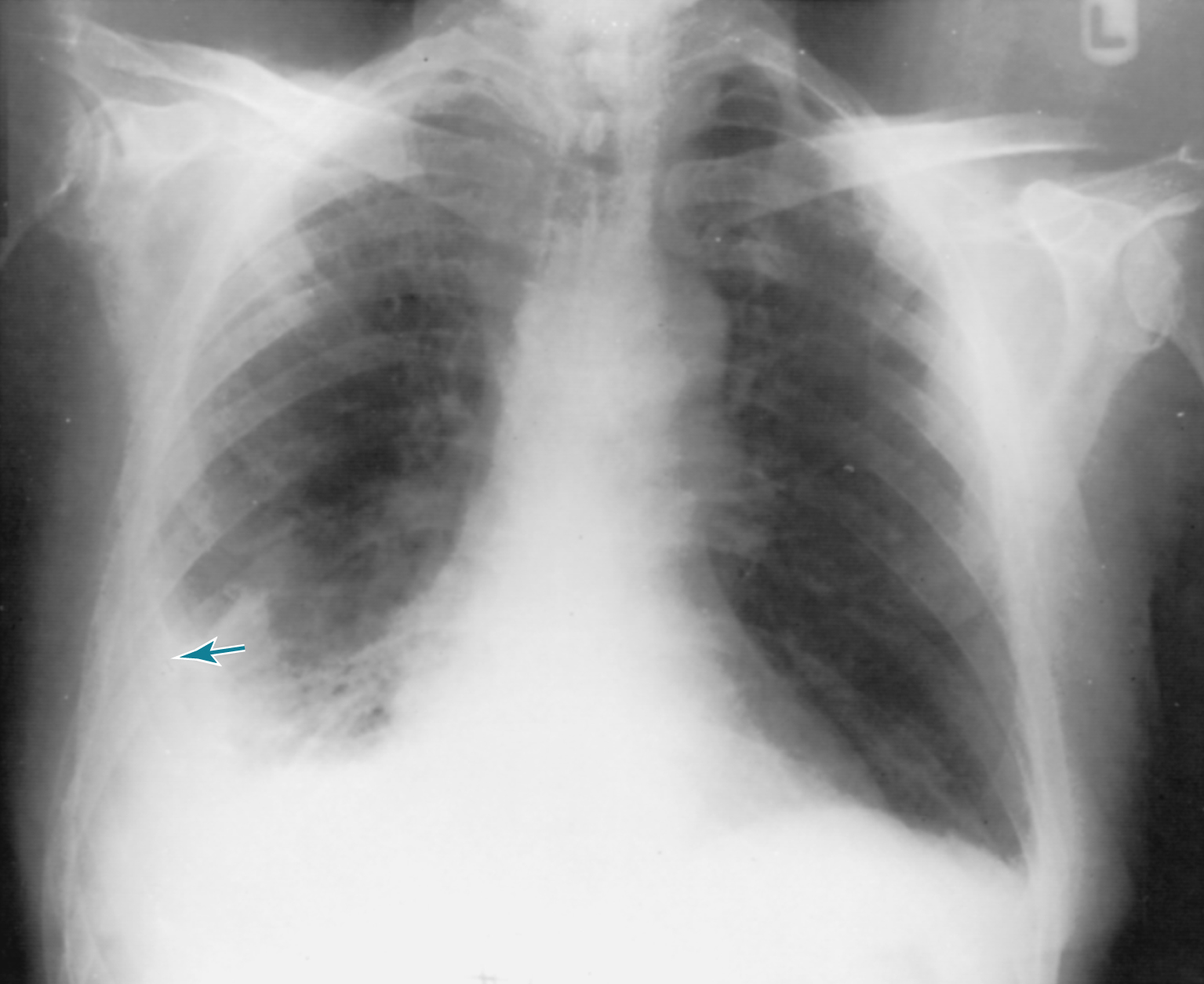
aspiration pneumonia, an inflammatory condition of the lungs and bronchi caused by inhaling foreign material or acidic vomitus. Compare bronchopneumonia. See also pneumonia. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Aspiration pneumonia may occur during anesthesia or recovery from anesthesia. At-risk patients include those with a decreased level of consciousness related to drugs and/or alcohol and those with swallowing difficulties or an impaired gag reflex. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Treatment depends on severity. Usual measures consist of prompt suctioning of the bronchi and administration of supplemental oxygen. Continued artificial ventilation may be required. Close monitoring of oxygenation status is imperative. The Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society Consensus Guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations for treatment. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: The patient’s pulse rate, quality of respirations, level of consciousness, and skin color are carefully monitored. Secretions are removed by suction as necessary. Infection and respiratory failure are frequent complications. Aspiration pneumonia may be prevented by positioning unconscious patients with the head elevated 15 to 30 degrees and turned to the side and by paying careful attention to the maintenance of enteral feeding therapy and an adequate airway. A comprehensive swallowing evaluation in patients with risk factors for aspiration pneumonia may prevent further episodes.