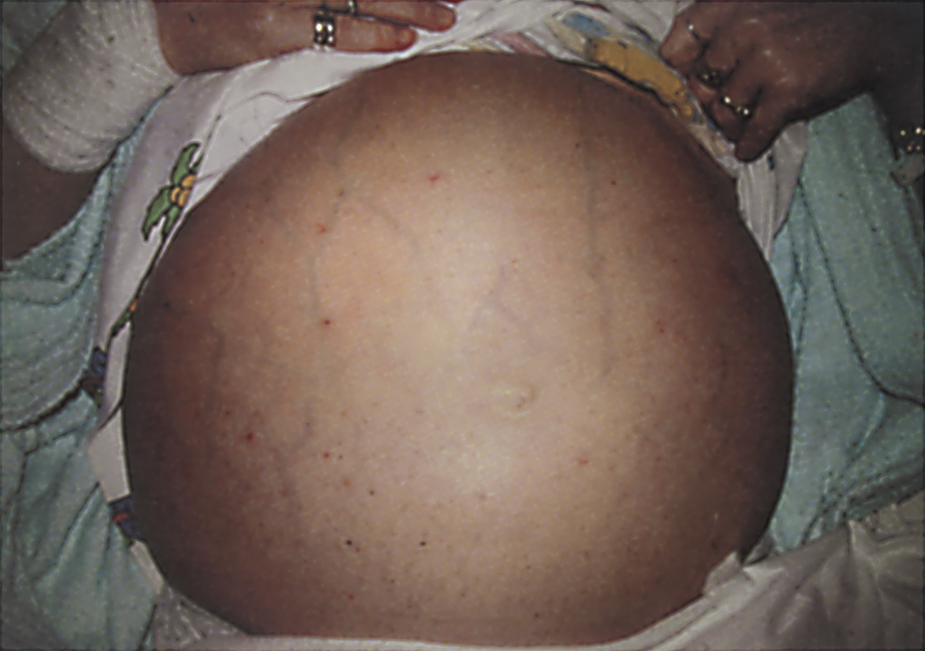
ascites /əsī″tēz/ [Gk, askos, bag] , an abnormal intraperitoneal accumulation of a fluid containing large amounts of protein and electrolytes. Ascites is a complication, for example, of cirrhosis, congestive heart failure, nephrosis, malignant neoplastic disease, peritonitis, or various fungal and parasitic diseases. See also paracentesis. −ascitic, adj. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Ascites may be observed when more than 500 mL of fluid has accumulated. Ultrasound examination can detect much smaller amounts. The condition may be accompanied by general abdominal swelling, hemodilution, edema, or a decrease in urinary output. Identification of ascites is made through palpation, percussion, and auscultation. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Ascites is treated with dietary therapy and diuretic drugs; abdominal paracentesis may be performed to relieve pain and improve respiratory and visceral function by relieving the pressure of the accumulated fluid. A peritoneovenous shunt may be surgically inserted to drain the ascites via a tube from the peritoneal cavity to the superior vena cava. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: The American Association for the Study of Liver Disease provides guidelines for ascites due to cirrhosis.