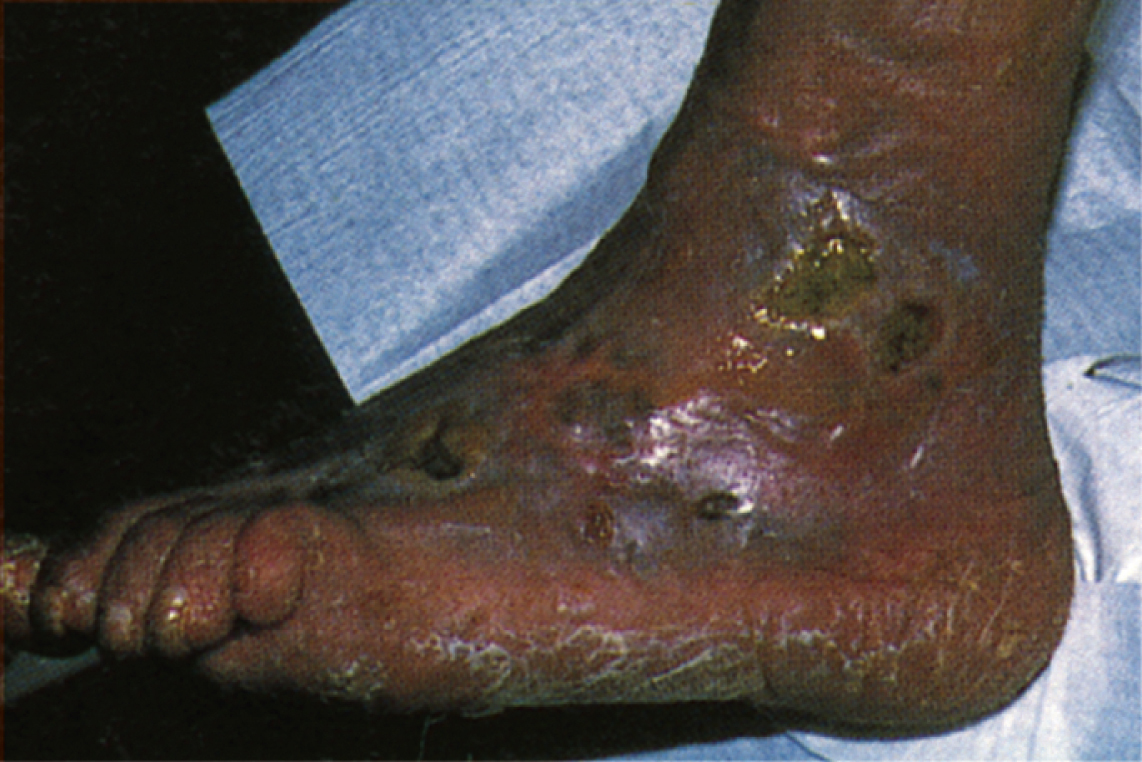
arterial insufficiency, inadequate blood flow in arteries. It may be caused by occlusive atherosclerotic plaques or emboli; damaged, diseased, or intrinsically weak vessels; arteriovenous fistulas; aneurysms; hypercoagulability states; or heavy use of tobacco. Signs of arterial insufficiency include pale, cyanotic, or mottled skin over the affected area, absent or decreased sensations, tingling, diminished sense of temperature, muscle pains, reduced or absent peripheral pulses, and, in advanced disease, arterial ulcers and atrophy of muscles in the involved extremity. Diagnosis includes checking and comparing peripheral pulses in contralateral extremities, angiography, ultrasound using a Doppler device, and skin temperature tests. Treatment may include a diet low in saturated fats, moderate exercise, sleeping on a firm mattress, use of a vasodilator, and, if indicated, surgical repair of an aneurysm or arteriovenous fistula. Use of tobacco products, prolonged standing, and sitting with the knees bent are discouraged.