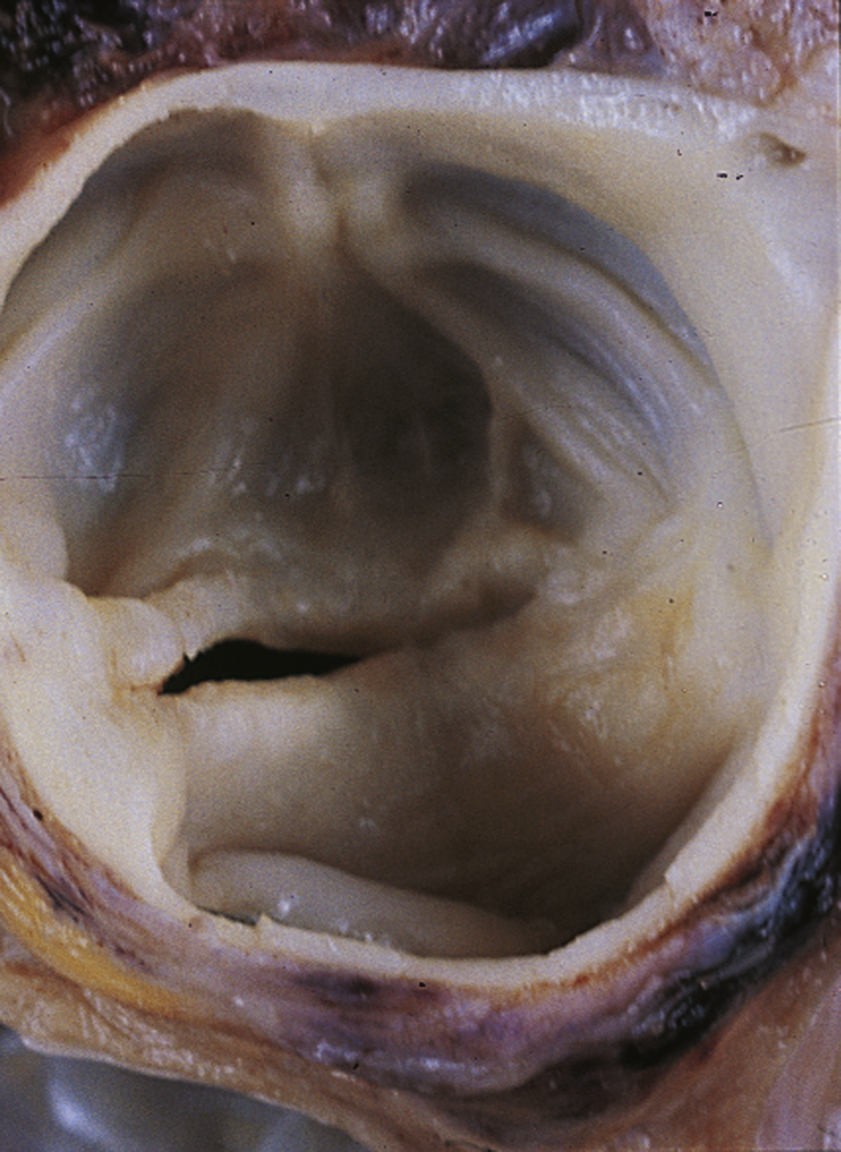
aortic stenosis (AS) [Gk, aeirein + stenos, narrow, osis, condition] , a narrowing or stricture of the aortic valve. Common causes include calcification of the valve because of age, congenital malformations such as bicuspid or unicuspid valves, or direct damage to the valve from rheumatic fever, which leads to fusion of the cusps. Surgical repair may be indicated. Surgery is followed by frequent examinations because prosthetic valve dysfunction and bacterial endocarditis are relatively common sequelae. See also congenital cardiac anomaly, valvular heart disease. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Aortic stenosis obstructs the flow of blood from the left ventricle into the aorta, causing decreased cardiac output and pulmonary vascular congestion. It may lead to congestive heart failure. Clinical manifestations include faint peripheral pulses, exercise intolerance, angina-type pain, syncope, and a harsh midsystolic murmur often introduced by an ejection sound. Diagnosis is confirmed by cardiac catheterization or echocardiography. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Surgical repair may be indicated. Surgery is followed by frequent examinations because prosthetic valve dysfunction and bacterial endocarditis are relatively common sequelae. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: Monitoring health and maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle are important. Children with aortic stenosis are usually restricted from strenuous activities, but should be encouraged to be active.