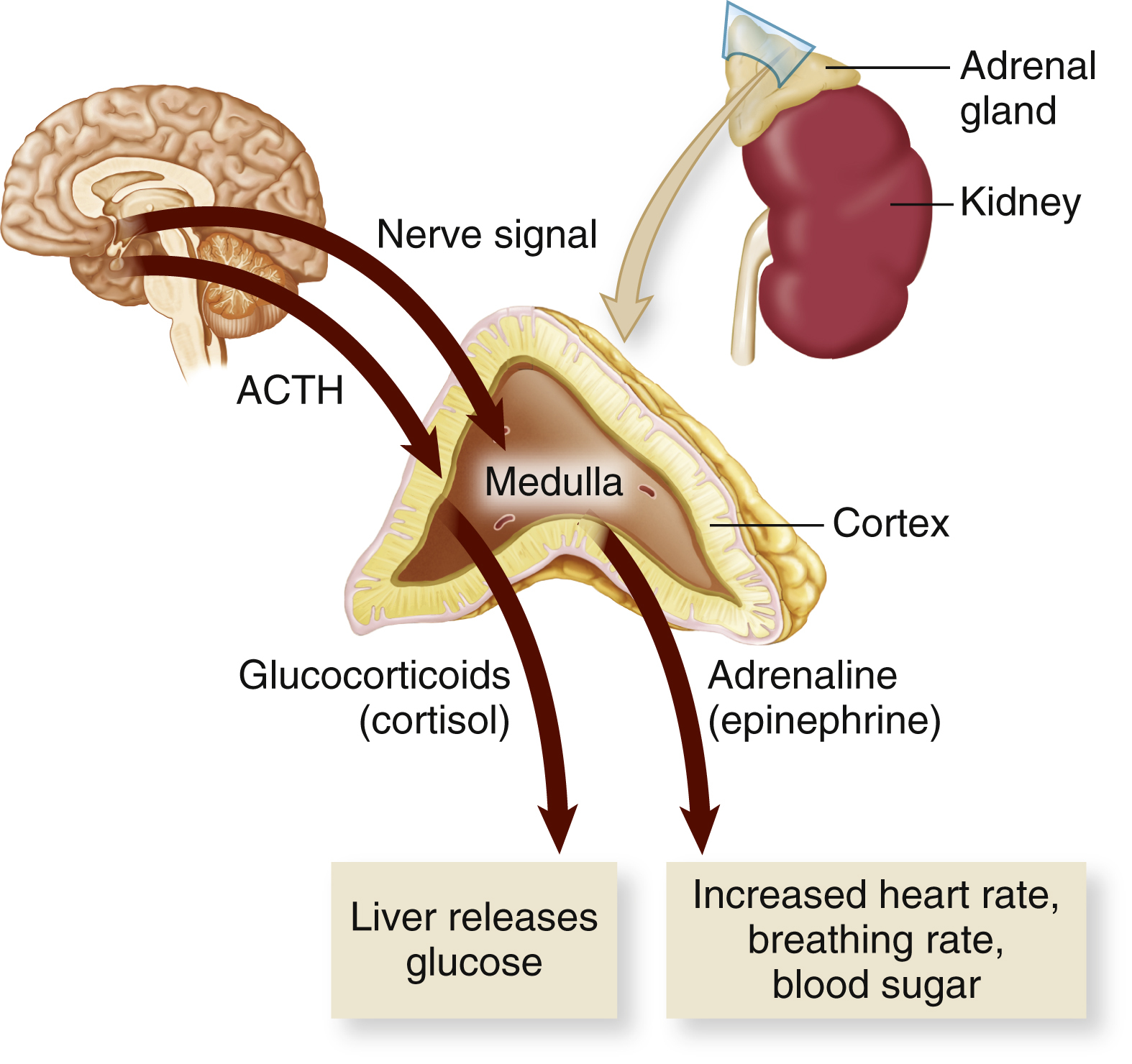
alarm reaction, the first stage of the general adaptation syndrome. It is characterized by the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) by the pituitary gland and of epinephrine by the adrenal medulla, which cause increased blood glucose levels and a faster respiration rate, increasing the oxygen level of the blood. These actions provide the body with increased energy for dealing with stress.