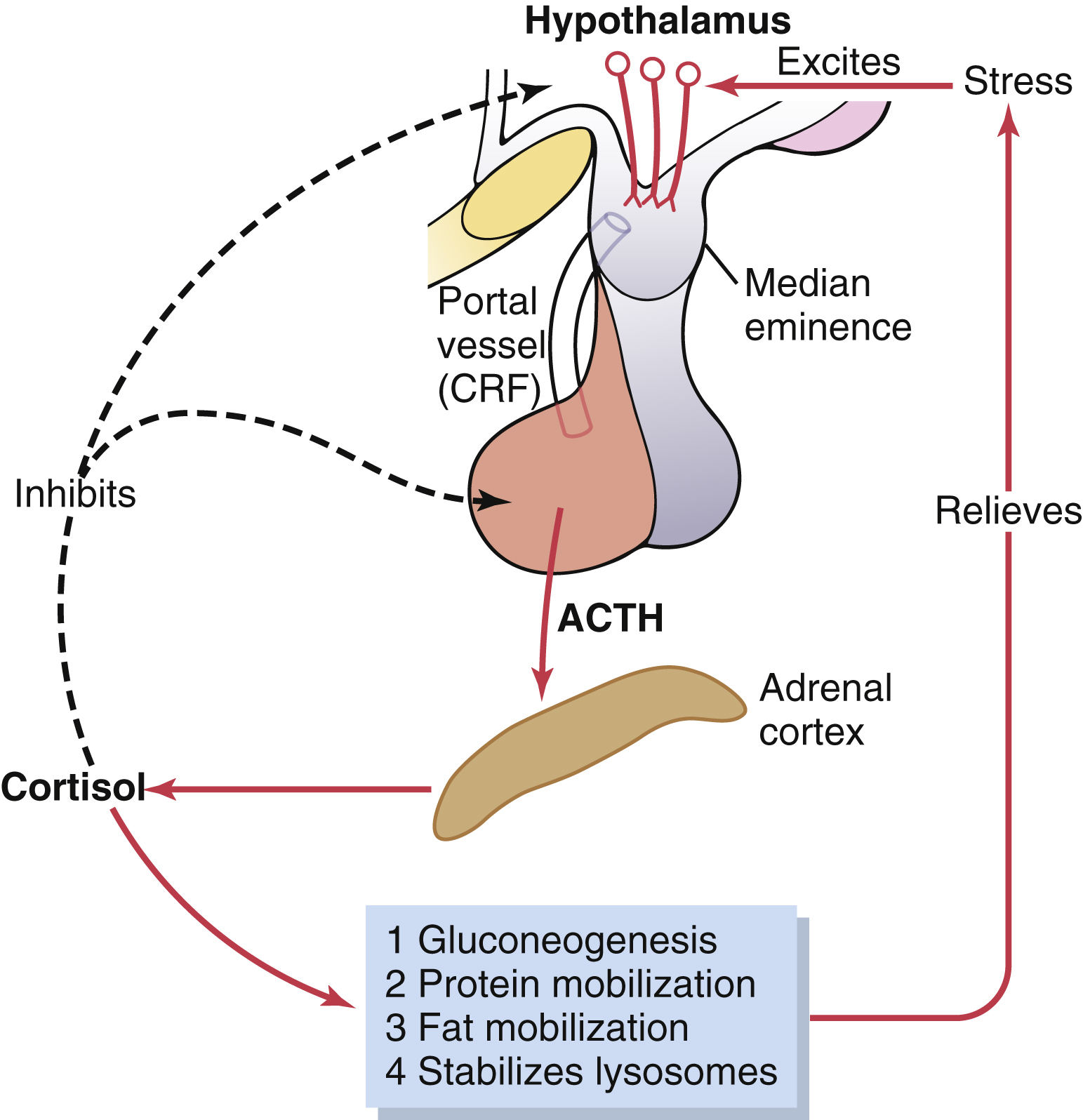
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), a hormone of the adenohypophysis that stimulates growth of the adrenal cortex and the synthesis and secretion of corticosteroids. ACTH secretion, regulated by corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus, increases in response to a low level of circulating cortisol and to stress, fever, acute hypoglycemia, and major surgery. Under normal conditions a diurnal rhythm occurs in ACTH secretion, with an increase beginning after the first few hours of sleep and reaching a peak at the time a person awakens and a low in the evening. ACTH may be used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and myasthenia. Normal ranges are from 15 to 100 pg/mL (10 to 80 ng/L) in the morning to less than 50 pg/mL (50 ng/L) in the evening. Normal values vary by laboratory. Also spelled adrenocorticotrophic hormone. See also corticotropin.