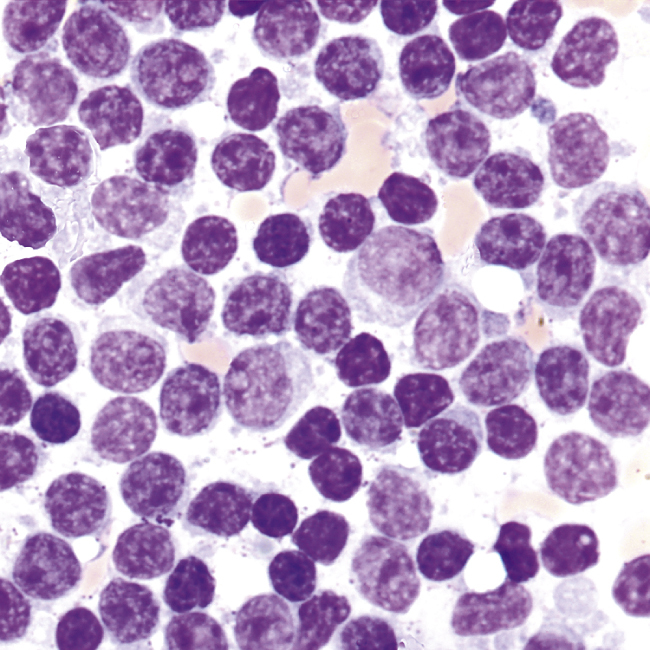
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) [Gk, chronos + L, lympha, water; Gk, kytos, cell, leukos, white, haima, blood] , a neoplasm of blood-forming tissues, characterized by a proliferation of small, long-lived lymphocytes, chiefly B cells, in bone marrow, blood, liver, and lymphoid organs. CLL is the rarest type of leukemia and the only leukemia to which there is a possible inheritable genetic predisposition. CLL is rare in persons less than 50 years of age, increases in frequency with age, and is more common in men than in women. The disease has an insidious onset and progresses to cause malaise, ready fatigability, anorexia, weight loss, nocturnal sweating, lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly. Most patients can continue normal activities for years; 25% die of unrelated diseases. No treatment is curative, but remissions may be induced by chemotherapy or irradiation. Compare acute lymphoblastic leukemia.