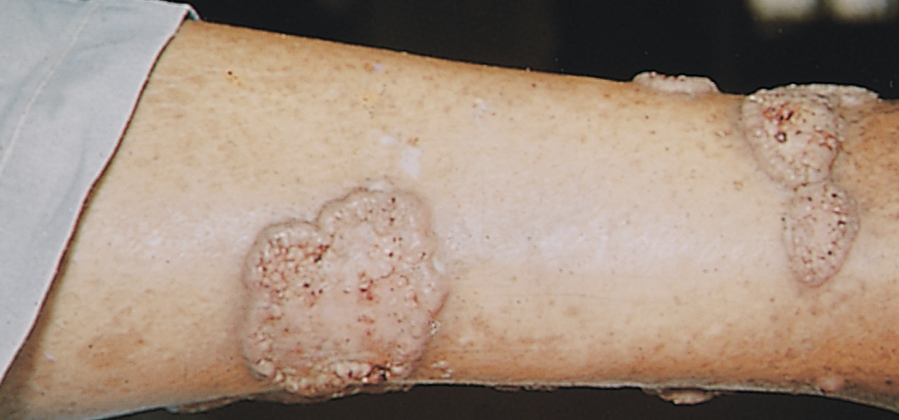
chromoblastomycosis /krō′mōblas′tōmīkō″sis/ [Gk, chroma + blastos, germ, mykes, fungus, osis, condition] , a chronic infectious skin disease caused by any multiple species to two genera of fungi Cladosporium and Phialophora found in the soil. Infection is characterized by the appearance of pruritic, warty nodules that develop in a cut or other break in the skin, occurring typically on the leg or foot. What may first appear as a small dull-red lesion gradually develops into a large ulcerated growth appearing like cauliflower tips in structure. Over a period of weeks or months additional warty growths may appear elsewhere on the skin along the path of lymphatic drainage. Common complications are secondary infection, lymphedema, and ulceration. Treatment includes surgical excision and, in some cases, topical application of systemic antibiotics. Flucytosine is the most commonly used antifungal agent. Also called chromomycosis, verrucous dermatitis. See also mycosis, specific fungal infections.