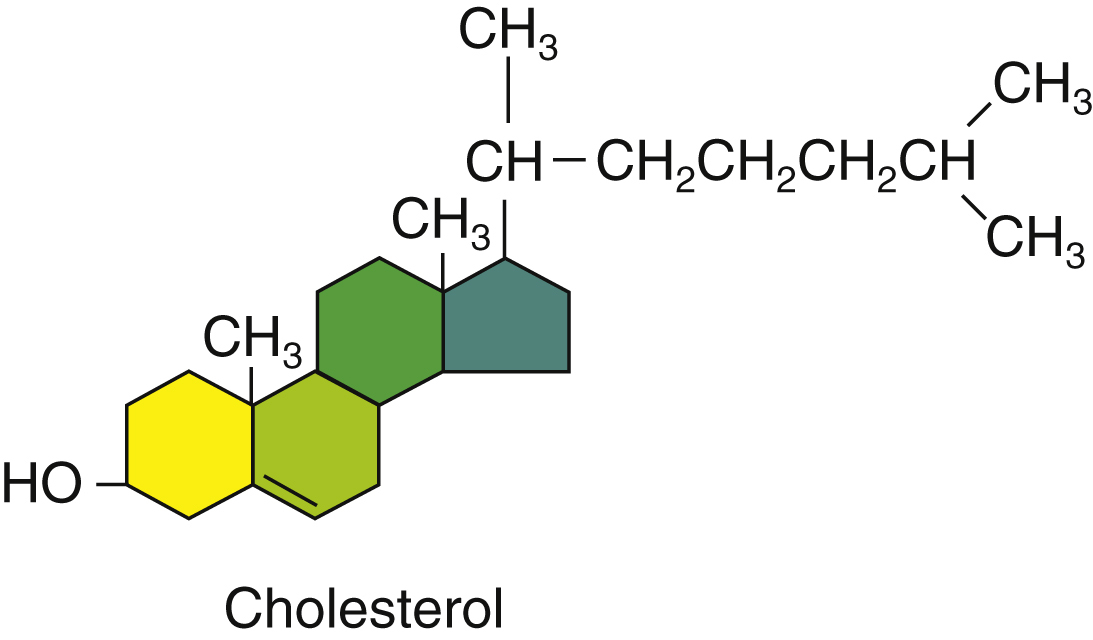
cholesterol /kəles″tərôl/ [Gk, chole + steros, solid] , a waxy lipid soluble compound found only in animal tissues. A member of a group of compounds called sterols, it is an integral component of every cell in the body. It facilitates the absorption and transport of fatty acids. Cholesterol acts as the precursor for the synthesis of various steroid hormones, including cortisol, cortisone, and aldosterone in the adrenal glands, and of the sex hormones progesterone, estrogen, and testosterone. It sometimes precipitates along with other compounds in the gallbladder to form gallstones. Cholesterol is found in foods of animal origin and is continuously synthesized in the body, primarily in the liver. Increased levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol may be associated with the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, whereas higher levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol appear to lower the person’s risk for heart disease. Normal adult levels of blood cholesterol are 150 to 200 mg/dL or 3.9 to 5.2 mmol/L (SI units). Also called cholesterin. See also high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, sterol.