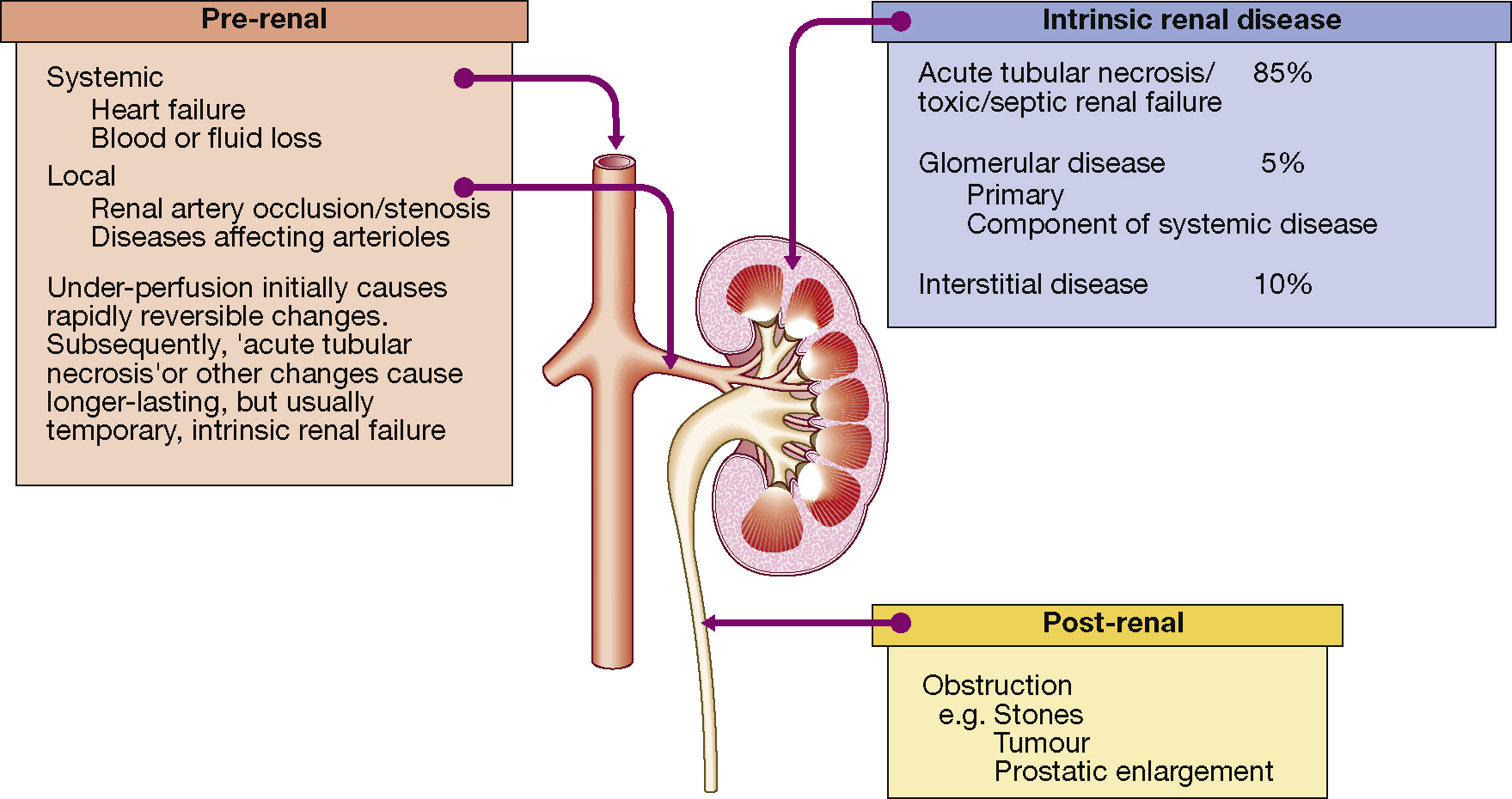
acute renal failure (ARF), renal failure of sudden onset, such as from physical trauma, infection, inflammation, or toxicity. Symptoms include uremia and usually oliguria or anuria, with hyperkalemia and pulmonary edema. Three types are distinguished: prerenal, associated with poor systemic perfusion and decreased renal blood flow, such as with hypovolemic shock or congestive heart failure; intrarenal, associated with disease of the renal parenchyma, such as tubulointerstitial nephritis, acute interstitial nephritis, or nephrotoxicity; and postrenal, resulting from obstruction of urine flow out of the kidneys. See also renal failure.