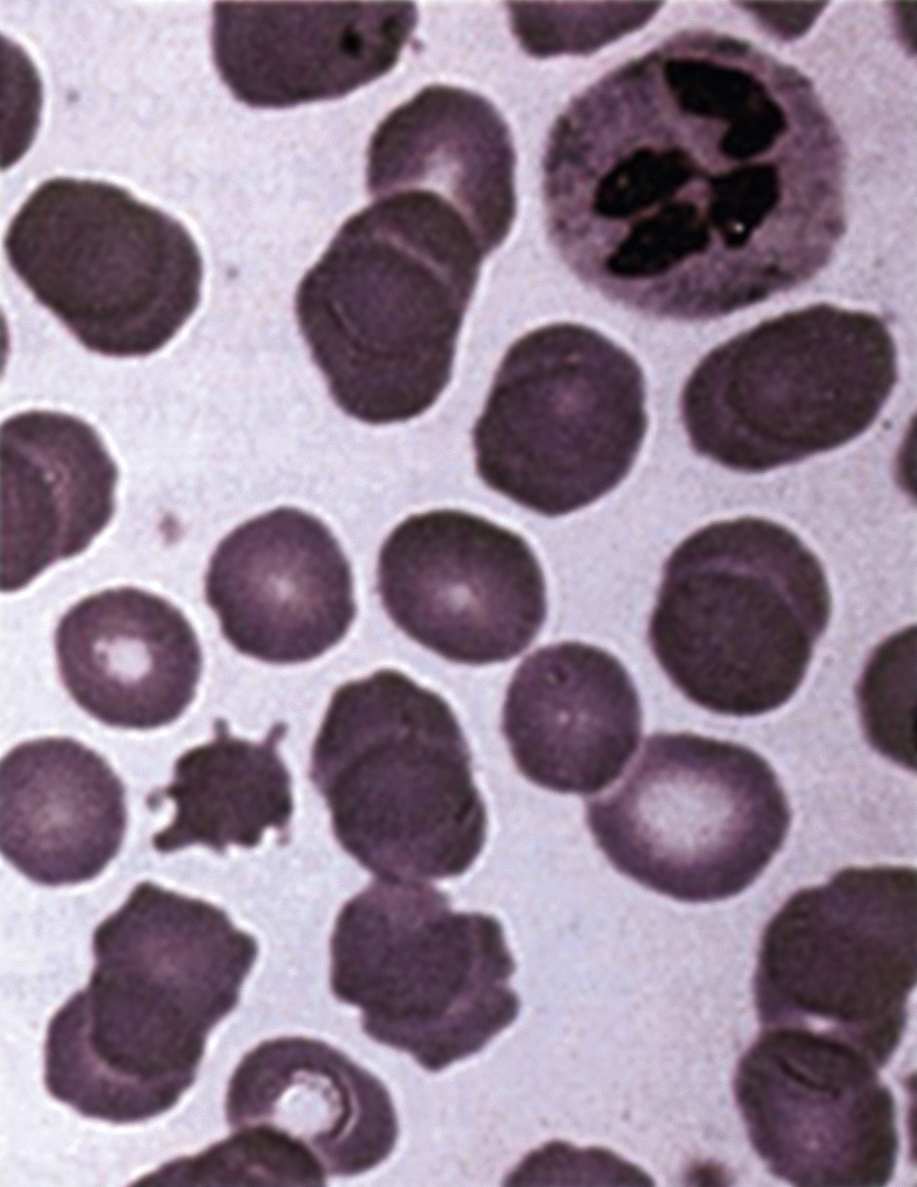
Chédiak-Higashi syndrome /ched″ē·ak·higä″shē/ [Moises Chédiak, 20th-century Cuban physician; Ototaka Higashi, 20th-century Japanese physician] , a congenital autosomal-recessive disorder, characterized by partial albinism, photophobia, pale optic fundi, massive leukocytic inclusions, psychomotor abnormalities, recurrent infections, and early death. Antenatal diagnosis can be made by amniocentesis and tissue culture. Bone marrow transplantation from an HLA-matched sibling is the therapy of choice. Treatment includes acyclovir, high-dose intravenous gamma globulin, and microtubulytic drugs, such as vincristine, vinblastine, and colchicine.