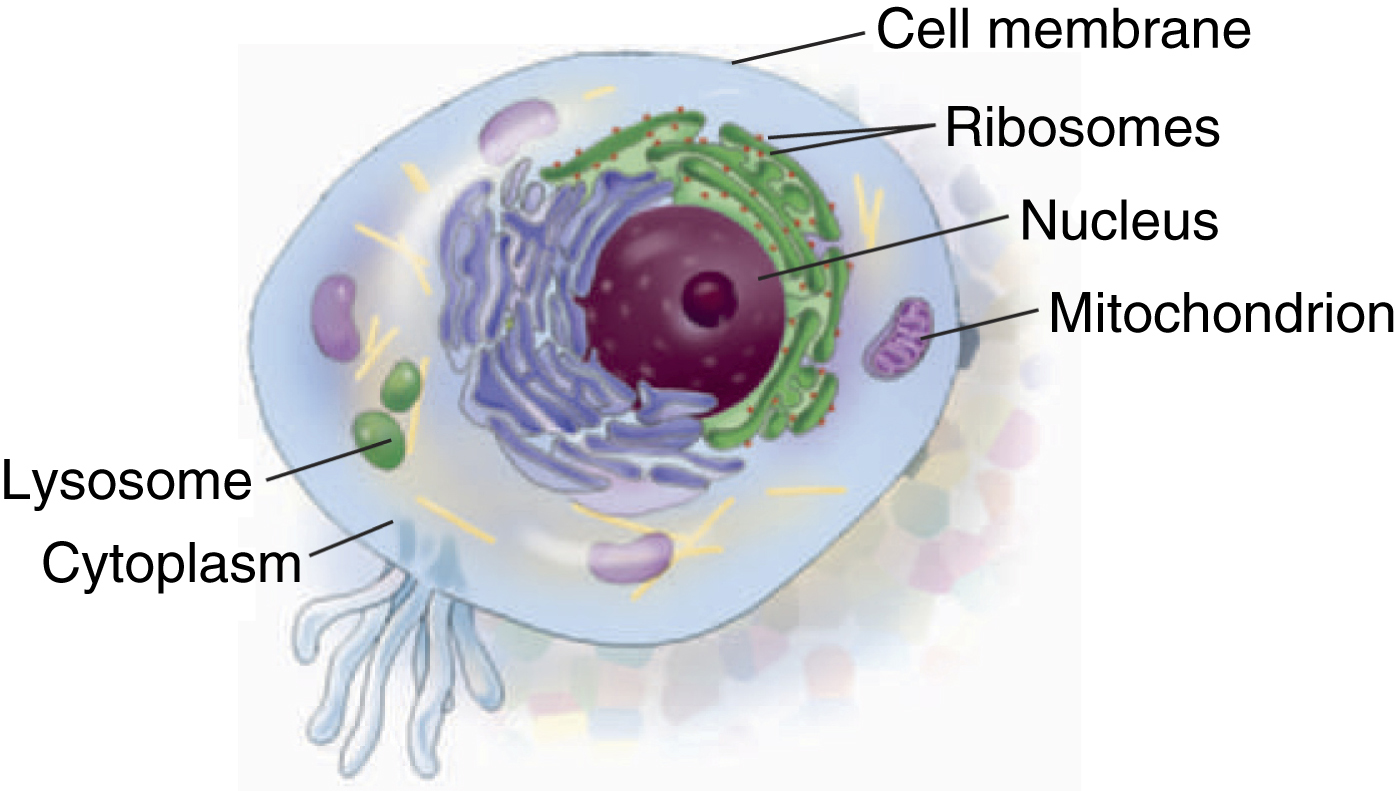
cell [L, cella, storeroom] , the fundamental unit of all living tissue. Eukaryotic cells consist of a nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles surrounded by a plasma membrane. Within the nucleus are the nucleolus (containing ribonucleic acid) and the chromatin (containing protein and deoxyribonucleic acid), which form chromosomes, wherein are located the determinants of inherited characteristics. Organelles within the cytoplasm include the endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, and centrosome. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells, even lacking a nucleus. The specialized nature of body tissue reflects the specialized structure and function of its constituent cells. See also cell theory. −cellular, adj.