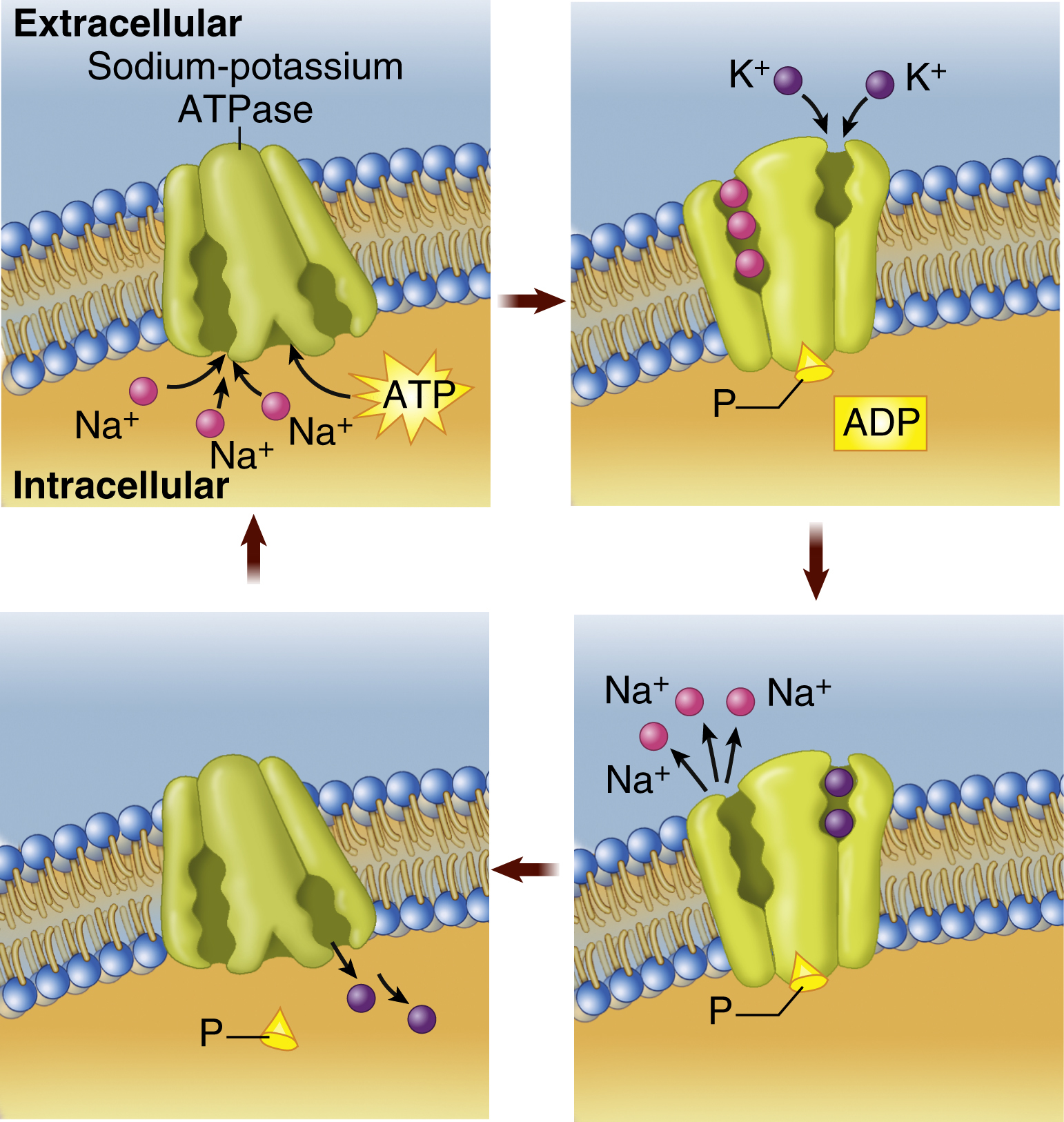
active transport, the movement of materials across the membranes and epithelial layers of a cell by means of chemical activity that allows the cell to admit otherwise impermeable molecules against a concentration gradient. Expediting active transport are carrier molecules within the cell that bind and enclose themselves to incoming molecules. Active transport is the means by which the cell absorbs glucose and other substances needed to sustain life and health. Certain enzymes play a role in active transport, providing a chemical “pump” that typically uses adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to help move substances through the plasma membrane. Compare osmosis, passive transport.