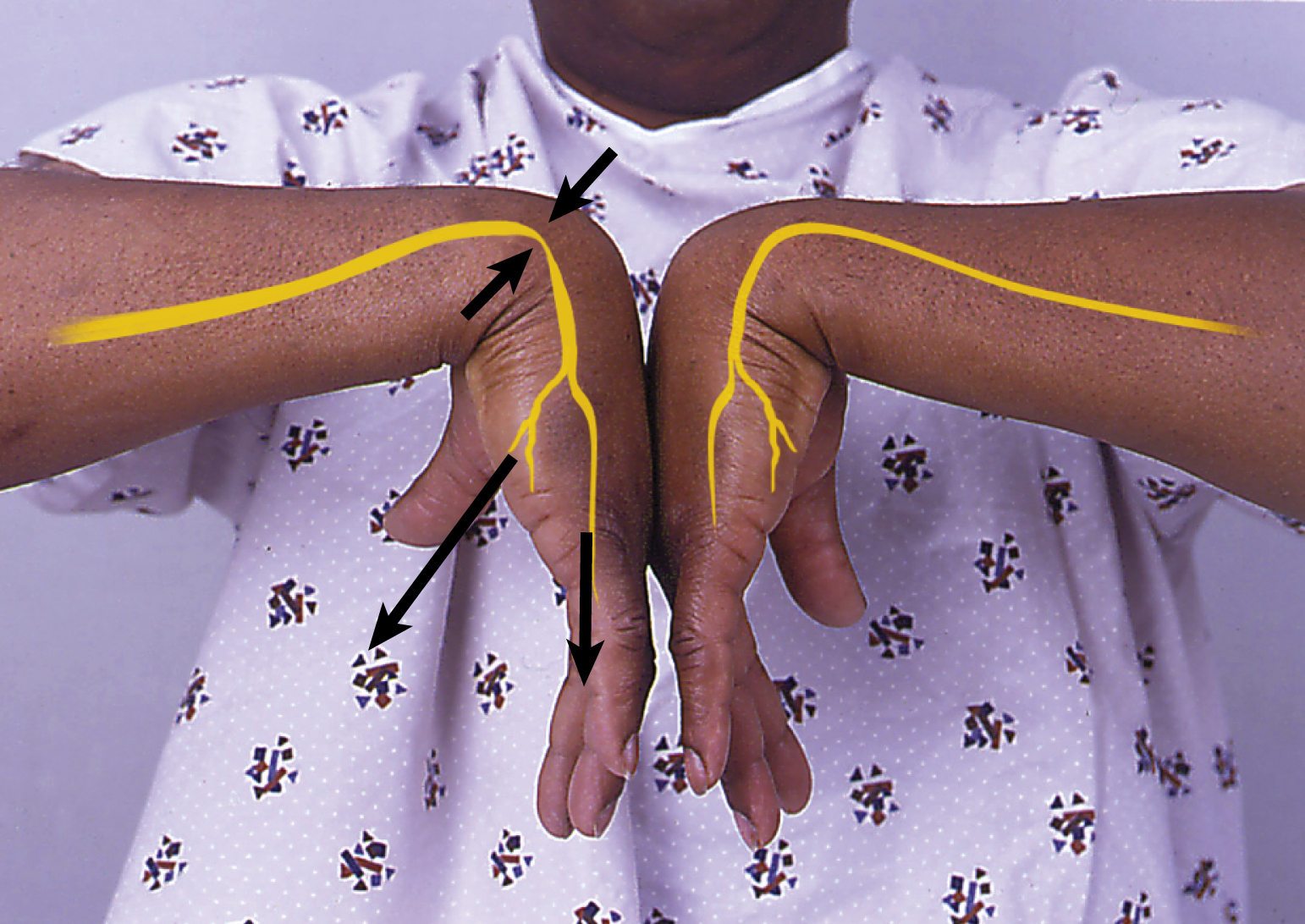
carpal tunnel syndrome, a common painful disorder of the wrist and hand, caused by compression on the median nerve between the inelastic carpal ligament and other structures within the carpal tunnel. It is often seen in cumulative trauma to the wrist. Symptoms may result from trauma, synovitis, or tumor or may develop with rheumatoid arthritis, amyloidosis, acromegaly, or diabetes. Symptomatic treatment usually relieves mild symptoms of recent onset, but if the pain becomes disabling, the injection of corticosteroids often yields dramatic relief. Surgical division of the volar carpal ligament to relieve nerve pressure is usually curative. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: The median nerve innervates the palm and the radial side of the hand; compression of the nerve causes weakness, pain with opposition of the thumb, and burning, tingling, or aching, sometimes radiating to the forearm and shoulder joint. Weakness and atrophy of muscles may increase from lack of use, as a result of pain that impairs thumb and finger dexterity. Pain may be intermittent or constant and is often most intense at night. Diagnosis can be confirmed by electromyography. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Symptomatic treatment usually relieves mild symptoms of recent onset, but if the pain becomes disabling, the injection of corticosteroids often yields dramatic relief. Patients with both severe and mild-to-moderate carpal tunnel syndrome benefit from wearing wrist splints. Surgical division of the volar carpal ligament to relieve nerve pressure is usually curative. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: There should be a thorough review of activities and the patient’s functional level in performing these activities. An occupational therapist or physical therapist should identify repetitive and/or resistive motions involving the wrist, as well as digital flexion and extension during activity. It is also critical to identify poor body mechanics and posture and to provide instruction for correction.