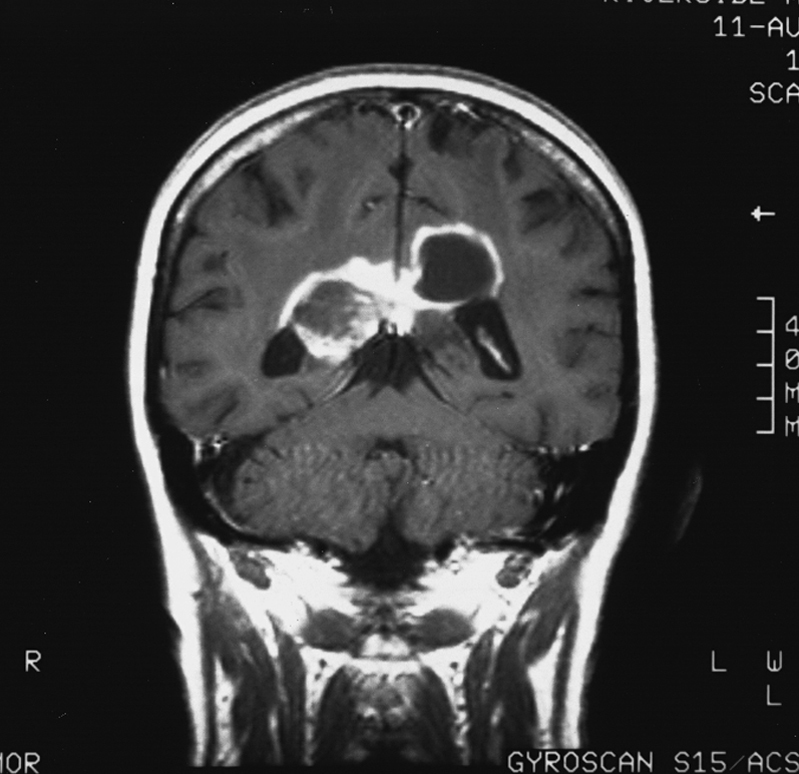
brain tumor, an invasive neoplasm of the intracranial portion of the central nervous system. Brain tumors cause significant rates of morbidity and mortality but are occasionally treated successfully. In adults 20% to 40% of malignancies in the brain are metastatic lesions from cancers in the breast, lung, GI tract, or kidney or a malignant melanoma. These are referred to as secondary tumors. The origin of primary brain tumors is not known, but the risk is increased in individuals exposed to vinyl chloride, in the siblings of cancer patients, and in recipients of renal transplantation being treated with immunosuppressant medication. Causes under investigation are genetic changes, heredity, ionizing radiation, environmental hazards, viruses, and injury. Gliomas, chiefly astrocytomas, are the most common malignancies. Medulloblastomas occur often in children. Surgery is the initial treatment for most primary tumors of the brain. Postoperative nursing care includes assessment of the patient to detect elevation in intracranial pressure. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Symptoms of a brain tumor are often those of increased intracranial pressure, such as headache, nausea, vomiting, papilledema, lethargy, and disorientation, but vary depending on the site of a tumor. Localizing signs, such as loss of vision on the side of an occipital neoplasm, may occur. Diagnostic measures include visual field and funduscopic examinations, skull x-ray examinations, electroencephalography, brain scanning, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, and spinal fluid studies. Cerebral angiography is used for information about vascular supply. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Radiotherapy is indicated for inoperable lesions, medulloblastomas, and tumors with multiple foci and is used in postoperative treatment of residual tumor tissue. The blood-brain barrier impedes the effect of some antineoplastic agents, but the administration of disk-shaped drug wafers is an emerging practice. A coordinated team approach to care will be dictated by the patient’s symptoms. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: A brain tumor can have a profound effect on activities of daily living. Symptoms are dependent on location and size.