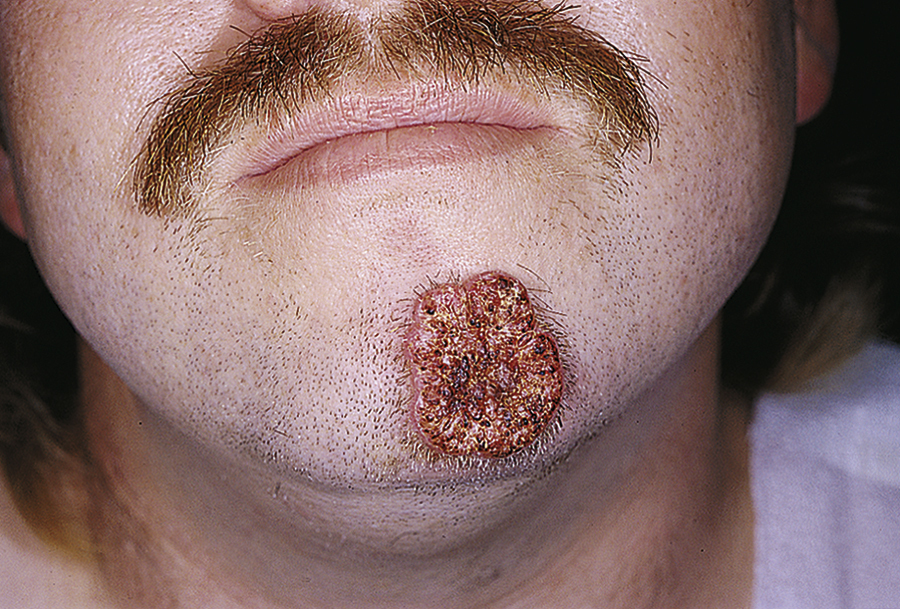
blastomycosis /blas′tōmīkō″sis/ [Gk, blastos + mykes, fungus, osis, condition] , an infectious disease caused by a yeastlike fungus, Blastomyces dermatitidis. It usually affects only the skin but may cause acute pneumonitis or disseminated disease and invade the lungs, kidneys, central nervous system, and bones. Also called Gilchrist’s disease. See also fungus, mycosis, North American blastomycosis. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Skin infections are almost always a result of hematogeneous seeding from a primary infection and often begin as small papules on the hand, face, neck, or other exposed areas where there has been a cut, bruise, or other injury. The infection may spread gradually and irregularly into surrounding areas. Lung infection is caused by inhalation of airborne conidia. When the lungs are involved, mucous membrane lesions resemble squamous cell carcinoma. The person usually has a cough, dyspnea, chest pain, chills, and a fever with heavy sweating. Diagnosis is made by identification of the disease organism in a culture of specimens from lesions. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Treatment usually involves the administration of amphotericin B in pulmonary disease or itraconazole or ketoconazole. Recovery usually begins within the first week of treatment. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: The disease is most common in river valleys of North America, particularly in the southeastern United States, but outbreaks have occurred in Africa and Latin America. The mortality rate is approximately 5%.