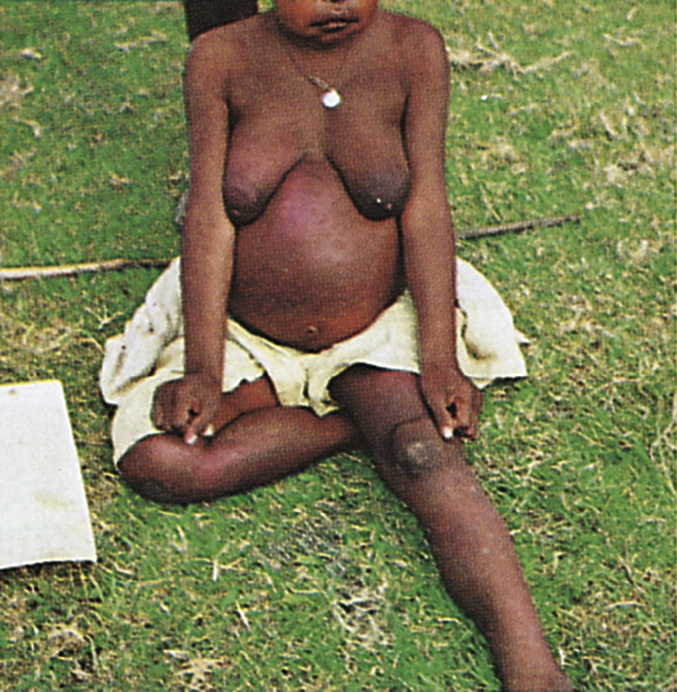
beriberi /ber′ēber″ē/ [Sinhalese, beri, weakness] , a disease of the peripheral nerves caused by a deficiency of or an inability to assimilate thiamine. It frequently results from a diet limited to polished white rice, and it occurs in endemic form in eastern and southern Asia. Rare cases in the United States are associated with stressful conditions, such as hypothyroidism, infections, pregnancy, lactation, and chronic alcoholism. Also called athiaminosis. See also thiamine. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Symptoms are fatigue, diarrhea, appetite and weight loss, disturbed nerve function causing paralysis and wasting of limbs, edema, and heart failure. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Administration of thiamine prevents and cures most cases of the disease. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: Beriberi is usually fatal if left untreated. With treatment, symptoms usually improve rapidly.