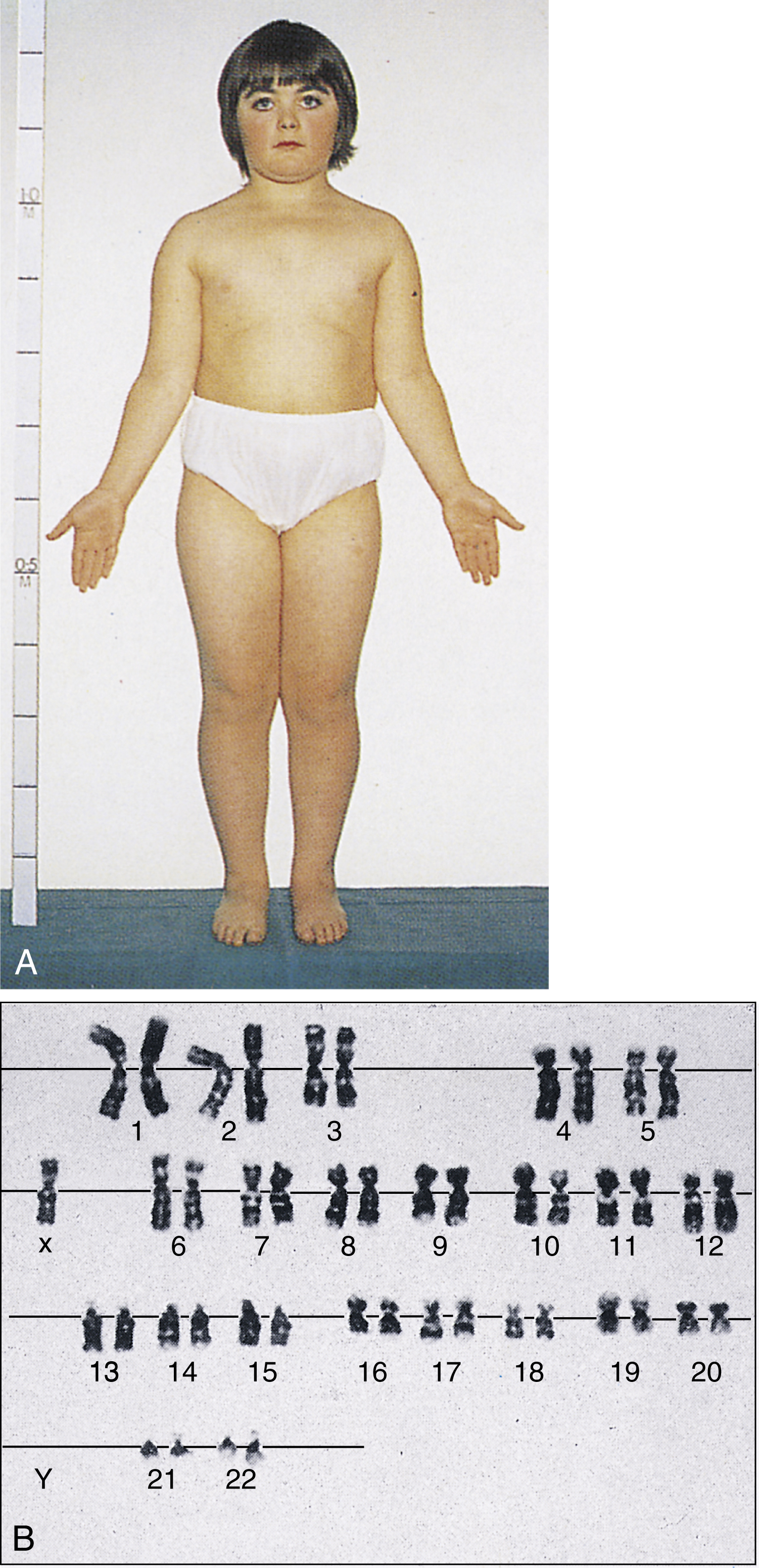
Turner’s syndrome [Henry H. Turner, American endocrinologist, 1892–1970] , a chromosomal anomaly seen in about 1 in 3000 live female births, characterized by the absence of one X chromosome; congenital ovarian failure; genital hypoplasia; cardiovascular anomalies; dwarfism; short metacarpals; “shield chest”; exostosis of tibia; and underdeveloped breasts, uterus, and vagina. Spatial disorientation and moderate degrees of learning disorders are common. Treatment includes genetic counseling, hormone therapy (estrogens, androgens, pituitary growth hormone), and often surgical correction of cardiovascular anomalies and the webbing of the neck skin. Also called Bonnevie-Ullrich syndrome, monosomy X. See also Noonan’s syndrome.