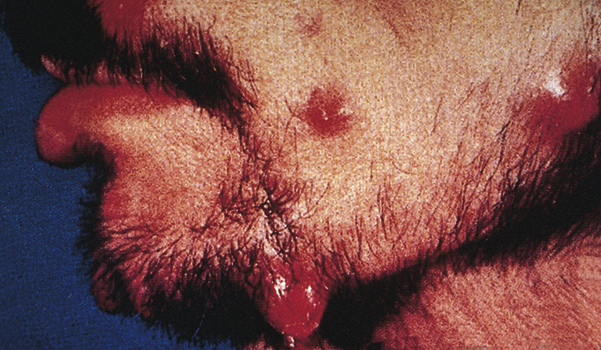
bacillary angiomatosis /bas″əler′ē/ , condition of multiple angiomata caused by an infection of Bartonella. The infectious agent is associated with contact with young cats infected with fleas and is also the cause of cat-scratch fever. It is manifested in persons with cellular immunodeficiency, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–infected patients, as small hemangioma-like lesions of the skin but may also involve the lymph nodes and viscera. The skin lesions are often mistaken for Kaposi’s sarcoma. Infection is curable but can be fatal if untreated. Treatments include oral erythromycin, tetracycline, trimethoprim, and rifampicin.