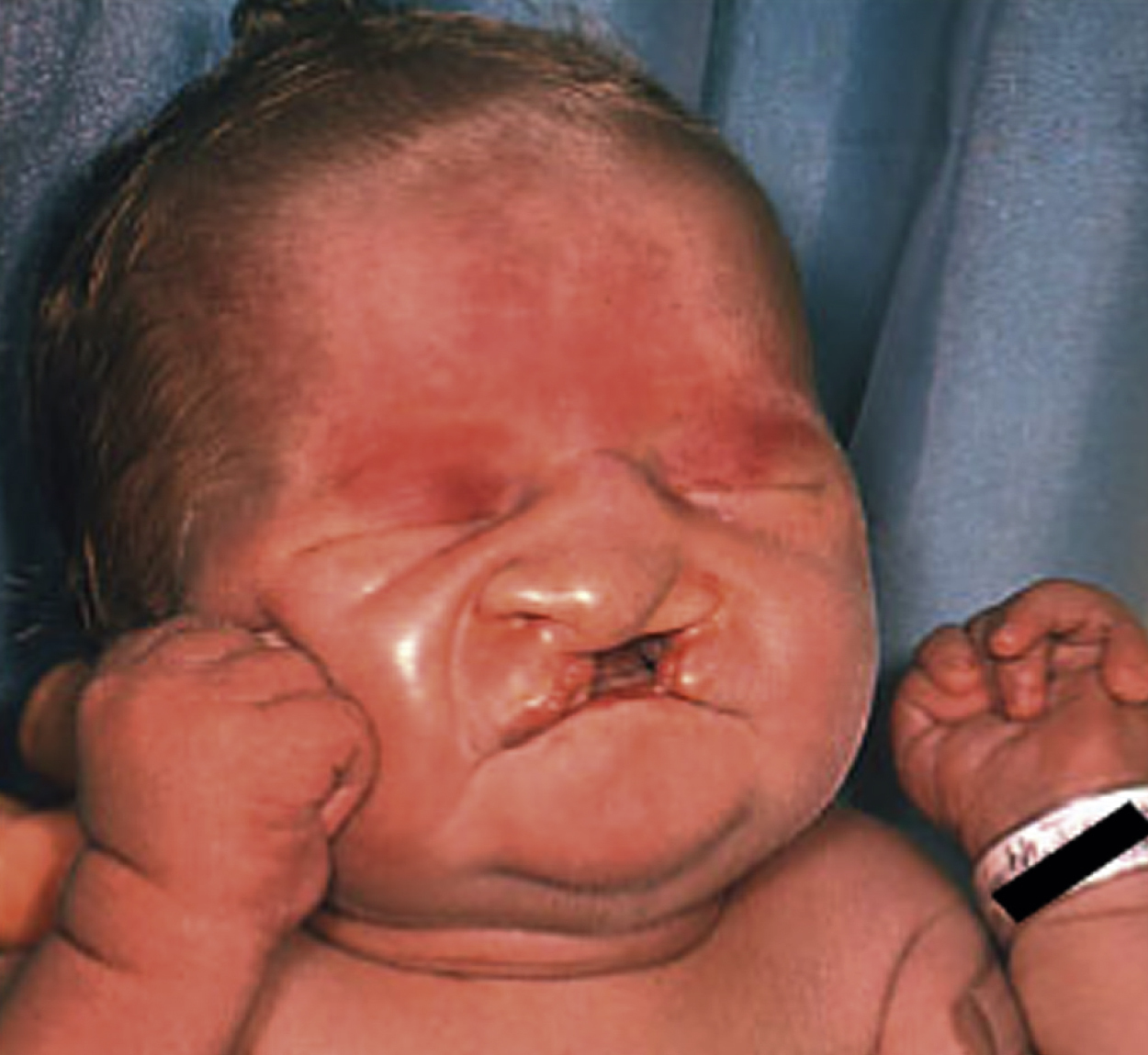
trisomy 13, a congenital condition caused by the presence of an extra chromosome in the D group, predominantly chromosome 13, although in rare instances chromosome 14 or 15. It occurs in approximately 1 in 5000 births and is characterized by multiple midline anomalies and central nervous system defects, including holoprosencephaly, microcephaly, myelomeningocele, microphthalmos, and cleft lip and palate. There is also severe cognitive impairment; polydactyly; deafness; convulsions; and abnormalities of the heart, viscera, and genitalia. Most infants with the condition are severely affected and do not survive beyond the first 6 months of life. The symptom combination of cleft lip and palate, polydactylism, and microcephaly is sometimes identified as the triad. Also called Patau’s syndrome, trisomy D syndrome, trisomy 13-15.