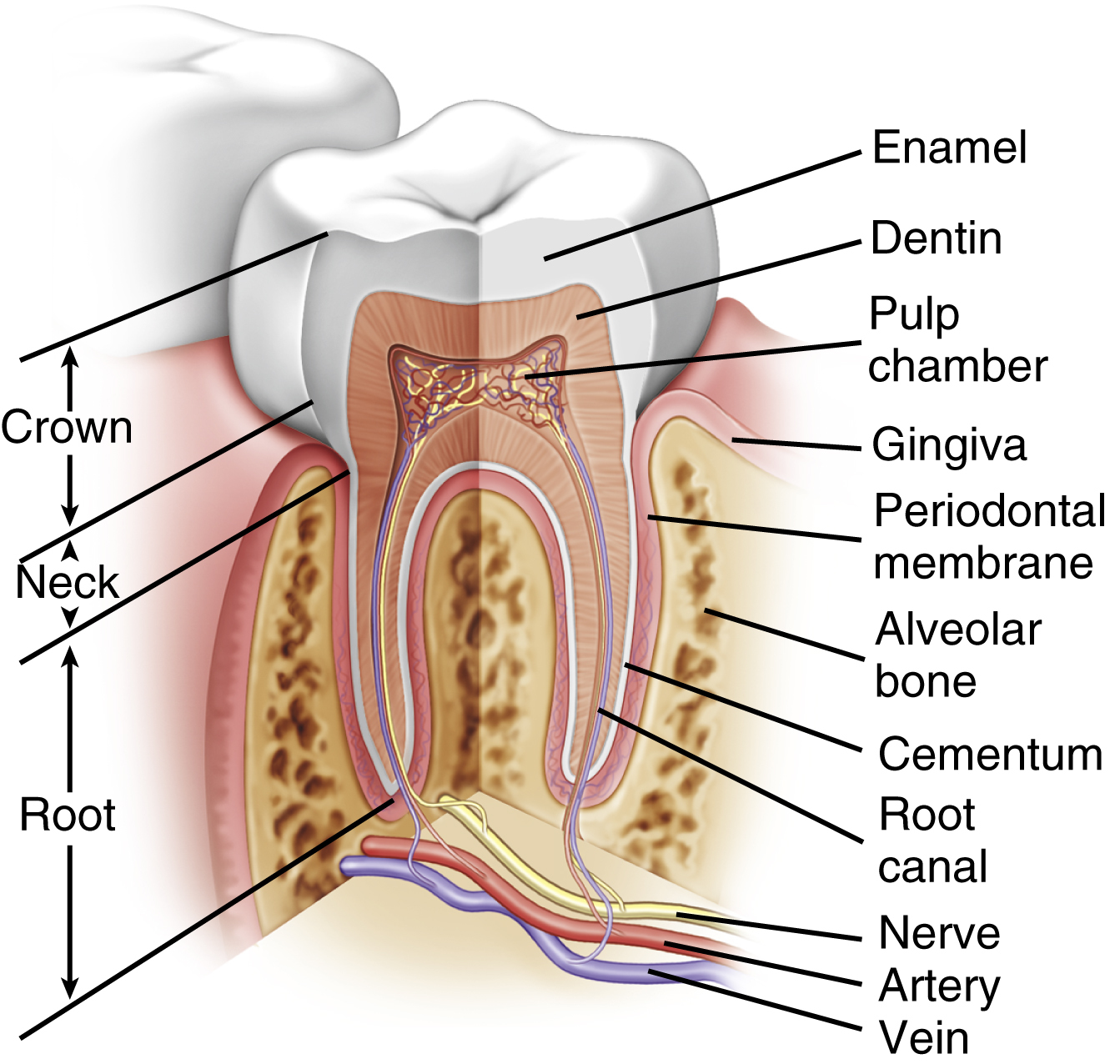
toothpl. teeth [AS, toth] , any one of numerous dental structures that develop in the jaws. Although derived from modified bone, they are typically classified as part of the digestive system and are used to cut and grind food in the mouth for ingestion. Each tooth consists of a crown, which projects above the gum; two to four roots embedded in the alveolus; and a neck, which stretches between the crown and the root. Each tooth also contains a cavity filled with pulp, richly supplied with blood vessels and nerves that enter the cavity through a small aperture at the base of each root. The solid part of the tooth consists of dentin, enamel, and a thin layer of bone on the surface of the root. The dentin composes the bulk of the tooth. The enamel covers the exposed part of the crown. Two sets of teeth appear at different periods of life: the 20 primary teeth appear during infancy, the 32 secondary teeth during childhood and early adulthood. See also primary dentition, secondary dentition.