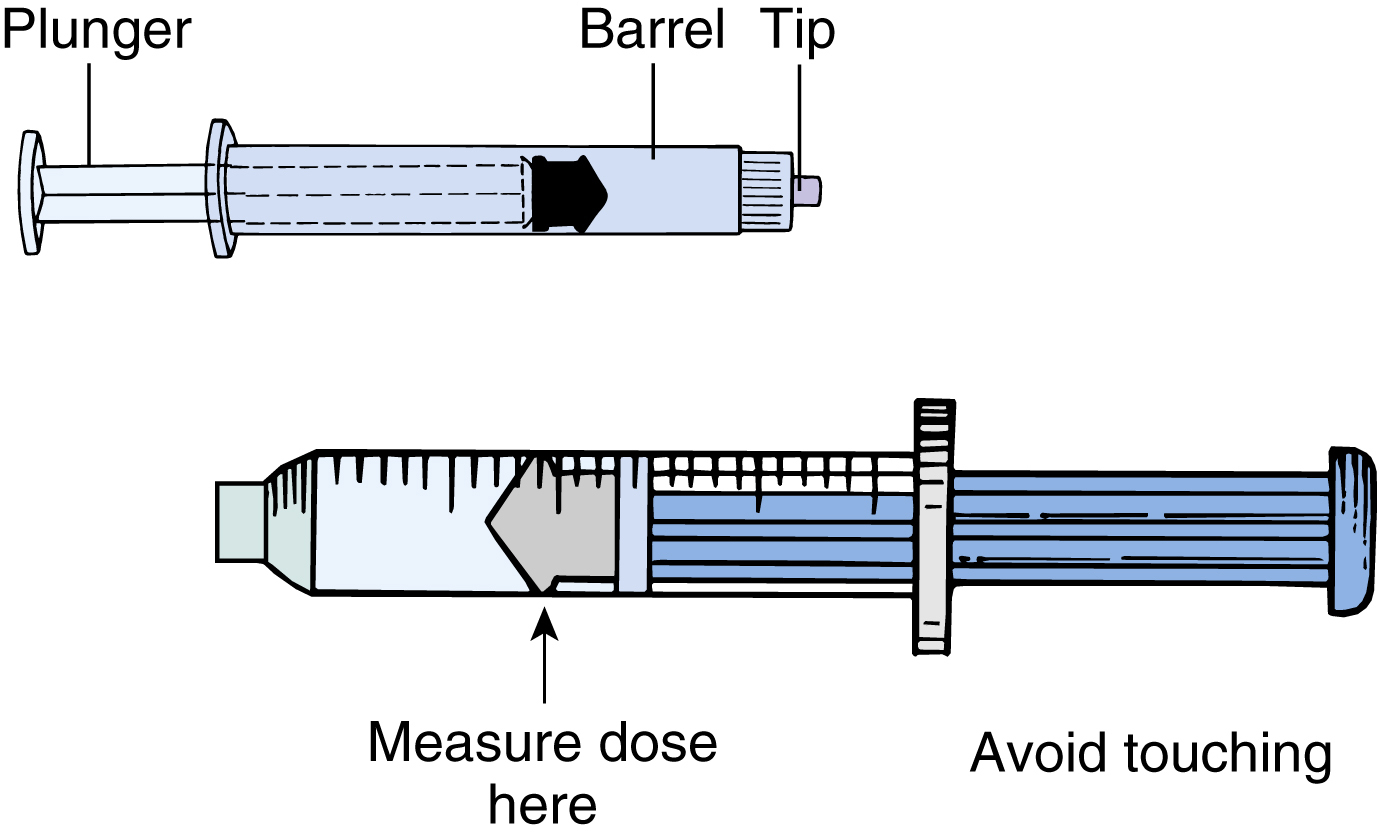
syringe /sərinj′, sir″inj/ [Gk, syrinx, tube] , a device for withdrawing, injecting, or instilling fluids. A syringe for the injection of medication usually consists of a calibrated glass or plastic cylindric barrel with a close-fitting plunger at one end and a small opening at the other to which the head of a hollow-bore needle is fitted. Medication of the desired amount may be pulled up into the barrel by suction as the plunger is withdrawn and injected by pushing the plunger back into the barrel, forcing the liquid out through the needle. A syringe for irrigating a wound or body cavity or for extracting mucus or another body fluid from an orifice or body cavity is usually larger than the kind used for injection. It often has a rubber bulb at one end and a blunt, soft-tipped flexible tube with an opening at the other end. The bulb is squeezed to eject a fluid and is released to withdraw one. Kinds include Asepto syringe, bulb syringe, hypodermic syringe, Luer-Lok syringe.